How powdered rock could help slow climate change
A method called enhanced rock weathering shows promise at capturing carbon dioxide from the air

A farmer in Scotland spreads rock dust on a field before cultivation. The pulverized rock could help pull excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and sequester it for thousands of years.
SO-Photography/Alamy Stock Photo
On a banana plantation in rural Australia, a second-generation farming family spreads crushed volcanic rock between rows of ripening fruit. Eight thousand kilometers away, two young men in central India dust the same type of rock powder onto their dry-season rice paddy, while across the ocean, a farmer in Kenya sprinkles the powder by hand onto his potato plants. Far to the north in foggy Scotland, a plot of potatoes gets the same treatment, as do cattle pastures on sunny slopes in southern Brazil.
And from Michigan to Mississippi, farmers are scattering volcanic rock dust on their wheat, soy and corn fields with ag spreaders typically reserved for dispersing crushed limestone to adjust soil acidity.
Across six continents, these farmers are experimenting with a technique called enhanced rock weathering, designed to improve degraded soils and help save the planet from climate doom.
Enhanced rock weathering takes advantage of Earth’s natural carbon cycle, which keeps carbon dioxide in perpetual rotation between air, water and soil. Volcanic rock naturally traps atmospheric CO2 in a process that transforms the gas into a solid form. Like a thermostat, rock weathering can slowly moderate Earth’s temperatures over geologic time by keeping atmospheric levels of CO2, a greenhouse gas, in check.
Over the last two decades, scientists the world over have studied how to accelerate weathering as a potential climate solution. Grinding volcanic rock into powder increases the surface area available for trapping CO2. While this rock dust can theoretically be spread anywhere, proponents typically target cropland, which offers easy access and multiple crop benefits.
Enhanced rock weathering is one of many carbon dioxide removal technologies that aim to strip the atmosphere of excess carbon dioxide. Approaches that lock up carbon dioxide could be key to meeting climate goals, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels — a target of the 2015 Paris Agreement — would require the removal of 100 billion to 1,000 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide by the end of the century, the IPCC says.
Enhanced rock weathering could put a substantial dent in that quantity, a team of researchers in the United States reported last year in Earth’s Future. If applied to all arable lands on the planet, the method could remove up to 215 billion tons over the next 75 years, according to the team’s computer simulations. That’s a fifth of the IPCC’s maximum estimate for needed removals.
“Crushing rocks — it’s almost too dumb an idea. But it actually works,” says Adam Wolf, cofounder and chief innovation officer of Eion, an enhanced rock weathering start-up that appeared in Time magazine’s list of best inventions last year.
Enhanced rock weathering may sound like a no-brainer. But it faces significant obstacles, including fears of potential environmental contamination and the challenge of how to measure and verify the carbon removal. There’s also concern that this relative newcomer to climate change mitigation might shunt money from longer-standing priorities, like preserving forests and their carbon-absorbing trees (SN: 7/13/21).
Because some approaches to carbon dioxide removal have been embraced by the fossil fuel industry, critics also worry that supporting them will allow oil and gas producers to keep emitting rather than shifting to clean energy.
But the reality is that the world is far from achieving its emission-reduction goals and short on time. As the IPCC warns, both emission reductions and atmospheric carbon dioxide removal are needed now. The only sensible course is to stop engaging in turf wars and immediately embrace all climate solutions — even newcomers, says Gabrielle Walker, an author and scientist by training who has founded multiple carbon dioxide removal initiatives.
“If we don’t build climate removals to gigaton scale by 2030,” Walker says, “we cannot achieve our climate goals.”
How does enhanced rock weathering work?
Enhanced rock weathering relies on a process that’s even older than the dinosaurs: the breakdown and buildup of rock. Water droplets in the atmosphere combine with carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid. When the weak acid rains down on volcanic rock, silicate minerals in the rock dissolve. This weathering releases calcium, magnesium and other nutrients needed by plants and forms stable bicarbonate ions (molecules with a net electric charge). The bicarbonate, HCO3–, traps the carbon from the atmosphere.
Bicarbonate flows from groundwater into streams and eventually the ocean, where corals, clams and other critters use it to make their shells and skeletons. Upon dying, the animals sink to the ocean floor and are eventually recycled into Earth’s interior at subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath another. The carbon remains inside the planet for tens of thousands of years or longer before volcanoes shoot out clouds of CO2 and spew silicate-containing lava, starting the cycle anew.
Natural rock weathering captures about 1.1 billion tons of CO2 each year. In 1990, German-born physicist Walter Seifritz pointed out that weathering could help counter climate change. But little happened until 2006, when Dutch geochemist Olaf Schuiling suggested spreading highly reactive olivine, a mineral often found in volcanic rock, on land to pull excess CO2 from the air.
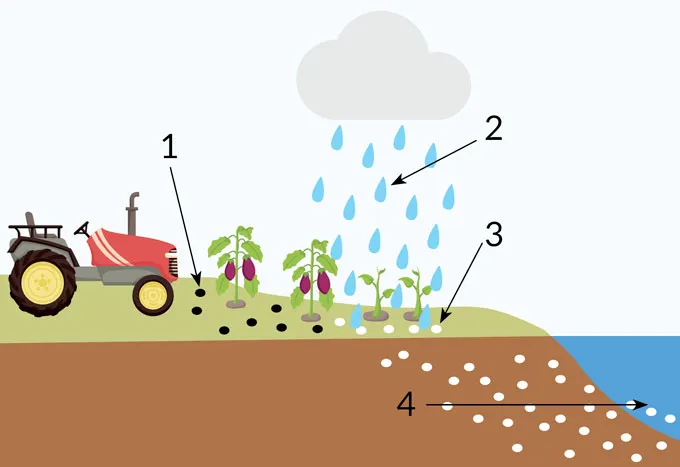
Weathering in action
With enhanced rock weathering, companies spread volcanic rock powder on cropland (Step 1 in illustration). Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere combines with water droplets to form carbonic acid (2). When that acid rains down on the rock powder, chemical reactions trap the acid’s carbon in bicarbonate (3), which eventually flows into the ocean (4).
Since then, research has boomed. Much of it has been spearheaded by the Leverhulme Centre for Climate Change Mitigation at the University of Sheffield in England, which has conducted studies in the lab and the field on multiple continents.
Spurred by promising results, dozens of enhanced rock weathering companies have formed in the last few years. Some already spread volcanic rock like basalt, some are in the trial phase and some are little more than a catchy web page. Most of these companies focus on cropland. They haul basalt from mines or quarries, grind it, transport it to farms and spread some 25 tons per hectare. Instead of basalt, the Irish company Silicate spreads leftover concrete, which is high in silicate. Companies provide the soil amendment to farmers for free, with the goal of generating revenue by selling carbon credits to large corporations such as Microsoft that want to offset their carbon footprints.
The Netherlands-based company greenSand takes a different approach, using olivine gravel for pathways and edging, driveways, decorative stones and bedding material to keep artificial turf springy.
Other companies are exploring the possibility of spreading rock dust on beaches and ocean waters, which could not only draw down carbon but potentially counter ocean acidification (SN: 4/26/24).
What are the benefits of enhanced rock weathering?
Enhanced rock weathering has multiple advantages over other forms of carbon dioxide removal, proponents say. The technique is built on a natural process, which may help lend credibility to the concept. It also builds on existing industrial processes — mining and agriculture — which can allow for rapid scale-up and reasonable expense.
All carbon dioxide removal methods require energy, land and water, and in these areas, enhanced rock weathering has a competitive edge over higher-tech methods like direct air capture and bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, an approach favored in Europe. That method involves growing crops such as sugar cane to absorb CO2 and then burning the plants, capturing the released carbon for storage underground and harnessing the heat for energy.
Energy needs for rock weathering, mostly related to the grinding and transport of rock, vary widely depending on parameters like distance to a farm and the fineness of the powder (using rock dust left over from mines can help save energy). In general, though, enhanced rock weathering typically requires only half as much energy as direct air capture, David Beerling, director of the Leverhulme Centre, and colleagues reported in 2022 in Communications Earth & Environment. The team studied carbon dioxide removal techniques in different countries.
A direct air capture plant uses massive fans and filters to suck CO2 out of the air. By one estimate, removing 1 billion tons of CO2 in this way would require about 1,200 terawatt-hours of electricity. That’s roughly three times as much electricity as the entire U.S. renewable sector generated in 2019.
“Crushing rocks — it’s almost too dumb an idea. But it actually works.”
Adam Wolf, cofounder and chief innovation officer of Eion
In addition to energy savings, enhanced rock weathering can complement existing land uses. That’s unlike some other carbon dioxide removal methods, such as bioenergy with carbon capture and storage. To achieve significant carbon removal, some researchers say this grow-and-burn strategy would need a total area of land larger than India. A study published in February in Science concluded that scaling up bioenergy with carbon capture and storage may “threaten food security and human rights…with potentially irreversible consequences.”
Another benefit of enhanced rock weathering is that it requires only a tenth or a hundredth as much water as direct air capture, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, and some other carbon dioxide removal strategies, Beerling and colleagues found.
Beyond climate benefits, enhanced rock weathering could help farmers. Modern agricultural practices — tilling soil, removing dead plant matter, monocropping, and applying pesticides, herbicides and synthetic fertilizers — have damaged soil structure, eroded fields and acidified soil. When soil becomes too acidic, essential nutrients can wash away, and microbes that help plants grow can be damaged. Overuse of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to the formation of nitrous oxide, a highly potent greenhouse gas (SN: 1/31/18).
Farmers already add crushed limestone to fields to raise soil pH. Volcanic rock powder has the same effect, and due to differences in chemical makeup, can remove more carbon from the atmosphere than limestone can. Volcanic rock powder can also release essential plant nutrients, add silicon (which may make plants more resistant to pathogens) and increase crop productivity. It even appears to reduce nitrous oxide emissions. Many of these benefits also come with regenerative agriculture techniques, such as no-till farming and the use of cover crops, that aim to improve soil health. Enhanced rock weathering is compatible with these techniques.
What are the downsides?
Although the mechanics of enhanced rock weathering are well understood, the potential long-term risks are not. The most serious concern is the potential for heavy metal accumulation in soils.
This concern was raised at last year’s United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP28 (SN: 12/15/23). Geochemist Gideon Henderson, chief scientific adviser at the U.K. Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, warned against rushing to embrace enhanced rock weathering approaches that involve pure olivine. “Olivine has high trace-metal content, including some toxins, and in the long term may cause significant negative environmental consequences,” Henderson said.
Heavy metals in olivine such as nickel can endanger health if absorbed at high enough levels by plants and ingested by humans (small amounts of nickel are essential for plant growth). Concerns about heavy metals arise from the fact that enhanced rock weathering works best with repeat applications, which can increase levels of the metals.
The study showing a 215-billion-ton reduction in atmospheric CO2 over a 75-year period assumes annual application of 10 tons of basalt per hectare. But one study, which assumed a commonly used application rate of 40 tons of basalt per hectare, suggests that safety limits for that level of application may be exceeded after only 10 years of repeat application.
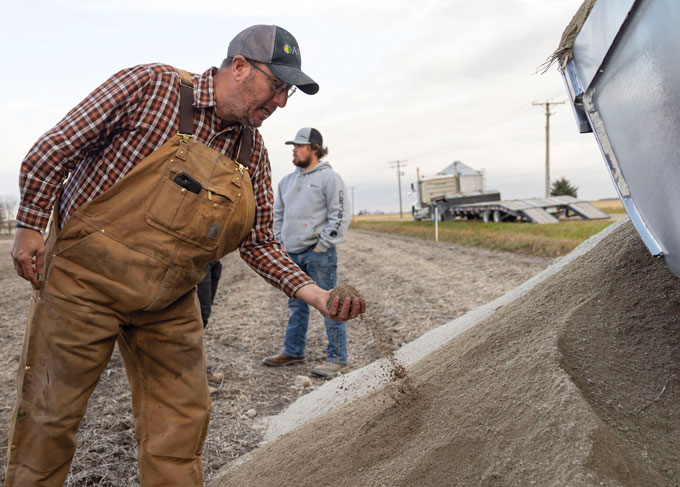

Eion, with projects located in the southeastern United States, uses olivine. Wolf, the company’s cofounder and chief innovation officer, points out that soil nickel levels in that region are so low that nickel fertilizer is actually recommended. In addition, plants absorb nickel more readily in acidic soil, something that olivine corrects. “No paper I know of has ever shown an actual toxicity impact of olivine,” Wolf says, including one by Henderson.
Still, at least one start-up isn’t taking any chances. Metalplant, an offshoot of the climate think tank Climitigation, grows a nickel-absorbing crop on fields treated with volcanic rock powder. Then the company extracts the nickel from the plants with the aim to sell the metal.
There’s also the question of how adding volcanic rock powder or crushed concrete will affect soil microbes. Geochemist Frank McDermott of University College Dublin is the scientific lead at Silicate, the start-up that uses concrete powder. While the microbial community generally responds well to an increase in soil pH when agricultural lime is added, basalt and concrete bring different mineral and chemical makeups. Despite extensive work, he says, scientists still don’t know how the addition of these powders, perhaps in higher quantity than lime, will impact the ability of soil microbes to break down organic matter, which is essential to soil health.
“Soils have a big store of organic carbon, and the goal is to protect and increase it over time. But if you add material that’s external to the system, and the microbes there have never seen basalt or concrete before, how will they react?” McDermott asks.
Another unknown is the possible effect of these rock powders on the flora and fauna of adjacent lands, lakes or ponds, or on marine life if rock powder is sprinkled into the ocean.
How to measure and verify carbon dioxide removal
In the acronym-heavy world of carbon dioxide removal, one jumble of letters stands out above all others: MRV, for measurement, reporting and verification. Accurate MRV is essential to assessing a technique’s effectiveness and enabling companies to sell carbon credits.
But how do you measure something you can’t see? A direct air capture machine filters CO2 from the air and concentrates it in purified form, allowing for easier measurement. With enhanced rock weathering, there’s no way to directly measure how much CO2 is drawn down.
Companies currently use multiple methods of measurement. For instance, soil releases a certain amount of CO2 into the atmosphere through normal soil respiration. The application of rock powder lowers the percentage of CO2 released. Respiration can be measured to infer carbon removal. Bicarbonate levels in groundwater samples are another measurement, along with quantifying how much rock powder dissolves. Eion developed its own process by using a trace element within olivine that leaves a “fingerprint” after the rock breaks down.
Each approach comes with uncertainties, but using multiple methods together might help verify that carbon removal has happened and provides a close approximation of the amount.
Yet conducting these field measurements can be a burden for small start-ups trying to stay afloat. For that reason, many companies are turning to simulations to predict CO2 removal rates.
Skeptics of this method say that simulations can’t yet replicate the complexity of nature. Ecologist Benjamin Houlton of Cornell University was among the first researchers to conduct field studies on enhanced rock weathering with basalt. Carbon drawdown can be accurately measured in small, tightly controlled test plots, he argues. But “scaling those measurements to something as big as an acre or multiple acres or thousands of acres is still not possible. It’s just not there yet,” Houlton says.

“I think what we’re seeing is a collision between the start-up culture wanting things to work, wanting to believe things will work — and that’s so important — versus the scientific process, which is conservative, careful and calculated,” Houlton adds. “The truth is somewhere in the middle.”
Some researchers, however, point to simulations’ fundamental role in studying climate. “If you accept that models can be used to model arguably more complicated systems [like climate change], I think it’s not a giant leap to expect that we can get models that are good enough to determine rock weathering and carbon dioxide removal rate,” says geoengineer Mike Kelland of the Leverhulme Centre.
Perhaps one way to increase confidence in carbon removal estimates is to work with an independent rating institution. In 2022, Puro.earth, a carbon credit platform based in Finland, developed the first set of certification standards for enhanced rock weathering. Puro.earth hopes this will encourage companies to adopt uniform measurement methods and soothe nervous carbon credit buyers.
To sell enhanced rock weathering carbon credits, Puro.earth requires that a company provide field data that show two different signals of rock weathering, such as measurements of respiration and bicarbonate levels. Start-ups must also prove that carbonic acid, and not some other soil acid, weathered the rock. Companies also have to take quantifiable measurements of CO2 capture. And Puro.earth requires proof that fields don’t exceed guidelines for heavy metal contamination.
“Puro.earth is adamant in that only robustly quantified and verified carbon removals can be credited,” says Marianne Tikkanen, cofounder and head of standard at Puro.earth. “Any enhanced weathering project must [verify] their soil conditions and explicitly and conservatively quantify the effect of all the various uncertainty factors and risks of reversal.”
Start-ups in North America, South America, the United Kingdom and India are using Puro.earth’s methodology. And in April 2023, Microsoft bought the first carbon credits based on enhanced rock weathering under Puro.earth’s crediting system from the Scottish company UNDO.
The future
Research on enhanced rock weathering is far from done. In a 2020 study published in Nature, Beerling and colleagues pinpointed the United States, China, India and Brazil as the major agricultural countries that are most suitable for immediate deployment of enhanced rock weathering. The strategy could help the United States and China offset up to 10 percent of their emission-reduction goals. For India, it’s 40 percent and for Brazil, it’s more than 100 percent.
Combining enhanced rock weathering with other strategies could lead to an even greater effect. Rock powder used alongside bioenergy with carbon capture and storage may improve the health of feedstock crops. And adding it to other nature-based methods can make agricultural land a more effective carbon sink.
“If we don’t build climate removals to gigaton scale by 2030, we cannot achieve our climate goals.”
Gabrielle Walker, author and scientist
To date, though, most government funding for carbon removal in the United States and Europe has gone to high-tech solutions like direct air capture. But that balance may be ever so slightly shifting. In May, the U.S. Department of Energy awarded five enhanced rock weathering projects, including Eion, $50,000 each to scale up the technology. And the European Union recently allowed enhanced weathering advocates to apply for consideration as an eventual removal strategy in Europe.
In this all-hands-on-deck moment, collaboration and open-mindedness may be key to avoiding the worst effects of climate change, Walker says. All carbon removal solutions need support. “This is not a zero-sum game,” she says. “This is an attempt to get to net-zero at the speed that we need.”






