
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Genetics
GeneticsIf you’re 35 or younger, your genes can predict whether the flu vaccine will work
A set of nine genes predicted an effective response to the flu vaccine in young people, no matter the strains.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth control research is moving beyond the pill
After decades of research, reproductive biologists are on the verge of developing new birth control options that stop sperm from maturing or save a woman's eggs for later.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new tool could one day improve Lyme disease diagnosis
There soon could be a way to differentiate between Lyme disease and a similar tick-associated illness.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore U.S. adults are drinking, and more heavily
Heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders have risen in the United States, at a cost to society’s health.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpread of misfolded proteins could trigger type 2 diabetes
Experiments in mice raise the question of whether type 2 diabetes might be transmissible.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMost football players who donated their brains to science had traumatic injury
A self-selected sample of 202 deceased football players, the largest to date, finds that the majority suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCows produce powerful HIV antibodies
For the first time in any animal, researchers elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV. Cows’ antibodies could help with drug development.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrinking sugary beverages in pregnancy linked to kids’ later weight gain
Consuming sugary drinks while pregnant may mean kids are heavier when they reach elementary school age.
-
 Health & Medicine
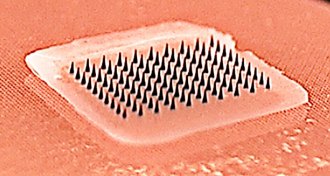
Health & MedicineGetting a flu ‘shot’ could soon be as easy as sticking on a Band-Aid
Microneedle patches may make home-based vaccination a reality.
-
 Health & Medicine
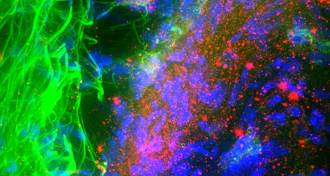
Health & MedicineProtein in Parkinson’s provokes the immune system
The immune system recognizes parts of a protein linked to Parkinson’s disease as foreign, triggering an autoimmune response.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew kind of ‘tan in a bottle’ may one day protect against skin cancer
A drug for activating melanin production without using ultraviolet radiation works in human skin samples.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen preventing HIV, bacteria in the vagina matter
Vaginal bacteria affect how well microbicide gels used to prevent HIV work.