Science Ticker
A roundup of research and breaking news
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeProtein linked to motor nerve cells being fast or slow
The protein, Delta-like homolog 1, is made in 30 percent of motor neurons and helps to determine at which speed the cells work, research shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
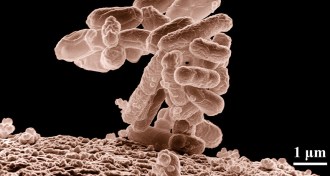
Health & MedicineImbalance in gut bacteria may play role in Crohn’s disease
Identifying the onset of Crohn’s disease may best be done by looking at bacteria in the cellular linings intestinal tissue.
-
 Tech
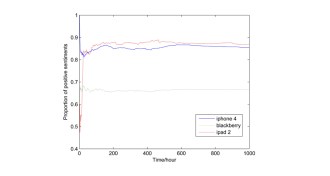
TechEarly advantages pay off in public opinion on Twitter
Twitter data show that having a slight advantage early in the formation of public opinion can be beneficial even though the state of the opinions level off over time.
-
 Earth
EarthHow the Chicxulub impact made acid rain
Using lasers to accelerate materials to asteroid-like impact velocities, scientists have shown how the Chicxulub asteroid impact, which happened roughly 65 million years ago, could have created a mass extinction in the oceans.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarm, wet weather may have helped Genghis Khan rule
Mild, wet weather — not drought — may have helped Genghis Khan expand the Mongolian empire to the largest in human history.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHeartbeats help people see
People were more likely to spot a flash of a hard-to-see ring when the image was presented right after a heartbeat
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMojave Crater may be source of many Martian meteorites
Many of the roughly 150 Martian meteorites found on Earth probably came from the Mojave Crater on Mars.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceAsteroid disintegrates while spinning too fast
Asteroid P/2013 R3 is shattering into a cloud of debris in these images captured by the Hubble Space Telescope.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dino species named Europe’s top predator
At up to 10 meters long and weighing in at four to five tons, this Tyrannosaurus rex-like beast could have been the biggest predator to ever roam Europe and among the largest dinosaurs to walk Earth during the late Jurassic period.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCosmic lens exposes spin of supermassive black hole
A chance alignment of a bright, distant galaxy behind a much closer one has given astronomers a rare opportunity to determine the spin of a supermassive black hole 6 billion light-years from Earth.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceSilk bone screws may mend better than metal ones
The silk-made screw and plates are less stiff than metal ones and dissolve in the body, making them a safer, less invasive alternative for setting broken bones.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFlying snakes get lift from surrounding air vortices
When a paradise flying snake leaps into and glides through the air, it’s getting lift from small, swirling vortices in the air around it.