Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Earth
EarthCritter-finding mission to Antarctica’s Larsen C iceberg scrapped
Thick sea ice ended a rapid-response mission to study seafloor that lay beneath Larsen C iceberg.
-
 Earth
EarthEarly land plants led to the rise of mud
New research suggests early land plants called bryophytes, which include modern mosses, helped shape Earth’s surface by creating clay-rich river deposits.
-
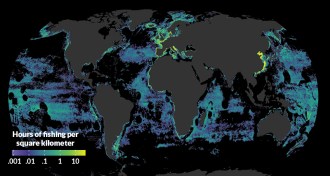 Earth
EarthNew mapping shows just how much fishing impacts the world’s seas
Industrial fishing now occurs across 55 percent of the world’s ocean area while only 34 percent of Earth’s land area is used for agriculture or grazing.
-
 Plants
PlantsThe flowers that give us chocolate are ridiculously hard to pollinate
Cacao trees are really fussy about pollination.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsStrong winds send migrating seal pups on lengthier trips
Prevailing winds can send northern fur seal pups on an epic journey.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHousehold products make surprisingly large contributions to air pollution
A study of smog in the Los Angeles valley finds that paints, fragrances and other everyday items are a growing component of the problem.
-
 Climate
ClimateLook to penguins to track Antarctic changes
Scientists say carbon and nitrogen isotopes found in penguin tissues can indicate shifts in the Antarctic environment.
-
 Life
LifeShipping noise can disturb porpoises and disrupt their mealtime
Noise from ships may disturb harbor porpoises enough to keep them from getting the food they need.
By Dan Garisto -
 Plants
PlantsAncient ozone holes may have sterilized forests 252 million years ago
Swaths of barren forest may have led to Earth’s greatest mass extinction.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHumans are overloading the world’s freshwater bodies with phosphorus
Human activities are driving phosphorus levels in the world’s lakes and other freshwater bodies to a critical point.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA peek into polar bears’ lives reveals revved-up metabolisms
Polar bears have higher metabolisms than scientists thought. In a world with declining Arctic sea ice, that could spell trouble.
By Susan Milius -
 Agriculture
AgricultureGrapevines are more drought-tolerant than thought
Grapevines handle drought better than previously thought. This could inform irrigation management.
By Dan Garisto