Genetics
-
 Life
LifeThe largest known genome belongs to a tiny fern
Though 'Tmesipteris oblanceolata' is just 15 centimeters long, its genome dwarfs humans’ by more than 50 times.
By Jake Buehler -
 Genetics
GeneticsHere’s why some pigeons do backflips
Meet the scientist homing in on the genes involved in making parlor roller pigeons do backward somersaults.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA genetic parasite may explain why humans and other apes lack tails
Around 25 million years ago, a stretch of DNA inserted itself into an ancestral ape’s genome, an event that might have taken our tails away.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAncient viruses helped speedy nerves evolve
A retrovirus embedded in the DNA of some vertebrates helps turn on production of a protein needed to insulate nerve cells, aiding speedy thoughts.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNewfound immune cells are responsible for long-lasting allergies
A specialized type of immune cell appears primed to make the type of antibodies that lead to allergies, two research groups report.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyGeneticist Krystal Tsosie advocates for Indigenous data sovereignty
A member of the Navajo Nation, she believes Indigenous geneticists have a big role to play in protecting and studying their own data.
By Joseph Lee -
 Genetics
GeneticsHow ancient herders rewrote northern Europeans’ genetic story
New DNA analyses show the extent of the Yamnaya people’s genetic reach starting 5,000 years ago and how it made descendants prone to diseases like MS.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFetuses make a protein that causes morning sickness in pregnancy
A hormone called GDF15 triggers a part of the brain involved in nausea and vomiting, a new study finds. Blocking its action may lead to treatments.
-
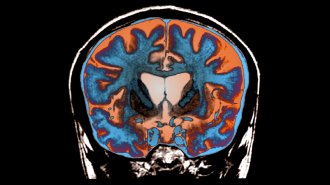 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy Huntington’s disease may take so long to develop
Repeated bits of the disease-causing gene pile up in some brain cells. New treatments could involve stopping the additions.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s how high-speed diving kingfishers may avoid concussions
Understanding the genetic adaptations that protect the birds’ brains when they dive for food might one day offer clues to protecting human brains.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThese 8 GMOs tell a brief history of genetic modification
Since the first genetically modified organism 50 years ago, GMOs have brought us disease-resistant crops, new drugs and more.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMost of today’s gene therapies rely on viruses — and that’s a problem
The next big strides in gene therapy for rare diseases may come from CRISPR and new approaches to delivery.