Genetics
-
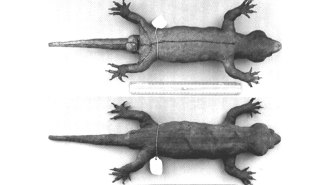 Animals
AnimalsDNA has revealed the origin of this giant ‘mystery’ gecko
A genetic analysis of a 19th century museum specimen, the only known example of the planet’s biggest gecko, has rewritten the animal’s backstory.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOctopuses and squid are masters of RNA editing while leaving DNA intact
Modifications to RNA could explain the intelligence and flexibility of shell-less cephalopods.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA rare mutation helped one man stave off Alzheimer’s for decades
The brain of a Colombian man with an inherited form of Alzheimer’s may hint at ways to halt or slow the progression of the disease.
By Simon Makin -
 Life
LifeThe new human pangenome could help unveil the biology of everyone
The deciphered DNA includes never-before-explored parts of the genome and better represents the genetic diversity of all humans.
-
 Life
LifeSwarming locusts can deploy a chemical to avoid being cannibalized
Releasing a “don’t-eat-me” pheromone signals a locust has become a toxic treat. The finding could lead to new ways to control destructive swarms.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHere are 5 cool findings from a massive project on 240 mammal genomes
A new series of studies on mammal genetics is helping scientists start to answer questions about evolution, cancer and even what makes us human.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsWhat was Rosalind Franklin’s true role in the discovery of DNA’s double helix?
Two researchers say that Rosalind Franklin knowingly collaborated with James Watson and Francis Crick to discover the molecular structure of DNA.
-
 Animals
AnimalsUrchins are dying off across the Caribbean. Scientists now know why
A type of single-celled microorganism associated with coral diseases is behind a sea urchin die-off in the Caribbean.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Animals
AnimalsOctopus, squid and cuttlefish arms evolved to ‘taste’ different compounds
Octopus suckers can taste a variety of greasy, sticky molecules, while squid and cuttlefish suckers detect bitter compounds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis sea cucumber shoots sticky tubes out of its butt. Its genes hint at how
A new genetics study is providing a wealth of information about silky, sticky tubes, called the Cuvierian organ, that sea cucumbers use to tangle foes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive yellow crazy ants create male ‘chimeras’ to reproduce
Yellow crazy ants are first known species where chimerism is required in males: Each of their cells holds DNA from just one of two genetic lineages.
-
 Life
LifeHow some beetles ‘drink’ water using their butts
Red flour beetles, a major agricultural pest, suck water out of the air using special cells in their rear ends, a new study suggests.
By Freda Kreier