Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNeandertals dove and harvested clamshells for tools near Italy’s shores
The discovery of sharpened shells broadens the reputation of Stone Age human relatives: Neandertals weren’t just one-trick mammoth hunters.
By Bruce Bower -
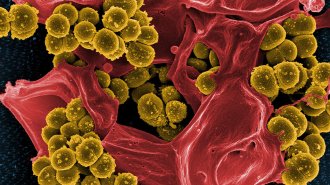 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes slowed by one drug can rapidly develop resistance to another
Hunkering down in a dormant, tolerant state may make it easier for infectious bacteria to develop resistance to antibiotics.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAfter the Notre Dame fire, scientists get a glimpse of the cathedral’s origins
Researchers will tackle the scientific questions behind rebuilding Notre Dame, and learn more about its history.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know — and don’t know — about a new virus causing pneumonia in China
A newfound coronavirus is behind a mysterious outbreak of pneumonia in central China. Experts urge vigilance but say there’s no cause for panic.
-
 Humans
HumansHomo erectus arrived in Indonesia 300,000 years later than previously thought
The extinct, humanlike hominid likely reached the island of Java by around 1.3 million years ago, a study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGlobal progress in combating child malnutrition masks problem spots
Low-resource countries are tackling serious childhood malnutrition, national-level statistics show, but a closer look highlights disparities.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineElectric scooter injuries rose 222 percent in 4 years in the U.S.
Hospital admissions from accidents related to e-scooters grew from 2014 to 2018.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealthy babies exposed to Zika in the womb may suffer developmental delays
A small group of Zika-exposed children in Colombia who were born healthy missed milestones for movement and social interaction by 18 months of age.
-
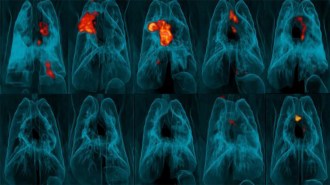 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInjecting a TB vaccine into the blood, not the skin, boosts its effectiveness
Giving a high dose of a tuberculosis vaccine intravenously, instead of under the skin, improved its ability to protect against the disease in monkeys.
By Tara Haelle -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA bioethicist says scientists owe clinical trial volunteers support
Researchers should be aware that many insurance policies do not cover experimental procedures, including side effects that may happen afterward.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn a first, an Ebola vaccine wins approval from the FDA
U.S. approval of Ervebo, already deployed in an ongoing Ebola outbreak in Congo, bolsters efforts to prepare for future potential spread of the disease.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesAirplane sewage may be helping antibiotic-resistant microbes spread
Along with drug-resistant E. coli, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.