Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika may harm nearly 1 in 7 babies exposed to the virus in the womb
A new CDC report tallies neurological and developmental problems, in addition to birth defects, possibly due to Zika in U.S. territory–born babies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists successfully transplant lab-grown lungs into pigs
Pigs implanted with lab-grown lungs recovered from surgery with no breathing problems.
-
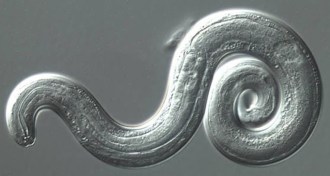 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRat lungworm disease is popping up in the mainland United States
A disease caused by a parasite endemic to Asia sickened at least 12 people in eight states in the continental United States from 2011 to 2017.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe ‘language gene’ didn’t give humans a big leg up in evolution
Scientists have long debated the role of a gene called FOXP2 in recent human evolution.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHurricane Maria’s death toll in Puerto Rico topped 1,100, a new study says
According to data from the Puerto Rico vital statistics system, Hurricane Maria killed an estimated 1,139 people.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsIndonesia’s pygmies didn’t descend from hobbits, DNA analysis suggests
Short people living on the Indonesian island of Flores don’t appear to have DNA from controversial, small-bodied Stone Age hominids called hobbits.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyCremated remains reveal hints of who is buried at Stonehenge
Ancient stone monument held burials of people from more than 200 kilometers away, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGoogle Glass could help children with autism socialize with others
Google Glass has a new lease on life, and this time it’s helping children with autism improve their social skills, a pilot trial suggests.
-
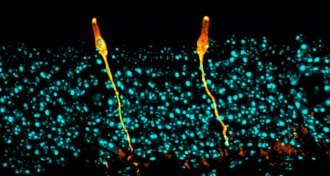 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNewfound airway cells may breathe life into tackling cystic fibrosis
A newly discovered cell in the lining of the airways is the primary site of activity for the gene that, when defective, causes cystic fibrosis.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA medical mystery reveals a new host for the rat lungworm parasite
Doctors report that A. cantonensis was transmitted to two people who ate raw centipedes, but you can get it from other creatures as well.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis tick may play a part in gumming up your arteries
Having antibodies to a sugar tied to red-meat allergy is associated with more plaque in the artery walls, a small study shows.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyConflict reigns over the history and origins of money
Thousands of years ago, money took different forms as a means of debt payment, archaeologists and anthropologists say.
By Bruce Bower