Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEven in the shade, a car’s interior can get lethally hot
A car’s interior can get lethally hot on summer days, even when it’s parked in the shade.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about the deadly Nipah virus
The deadly and rare Nipah virus has killed at least 11 people in southern India, causing concern among epidemiologists.
By Maanvi Singh -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnant bonobos get a little delivery help from their friends
As in humans, female bonobos become helpers for mothers giving birth, data from captive apes suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic sleuthing again IDs a murder suspect in a cold case
The arrest of a second murder suspect with the help of genetic genealogy raises worries that suspicionless searches may be next.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhat genetic tests from 23andMe, Veritas and Genos really told me about my health
A Science News reporter tried out three consumer genetic testing companies to see what people really learn about their health.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlack children commit suicide at twice the rate of white kids
The suicide rates for young black kids are higher than those of their white counterparts, a pattern that flips in older kids, researchers find.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola vaccinations begin in Congo
A vaccination campaign is up and running to fight the ongoing Ebola outbreak in Congo. It’s the first of its kind.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyGun owner or not, Americans agree on many ways to limit gun violence
A new survey suggests that gun owners support many potential gun-control policies — now research on their efficacy needs to catch up.
-
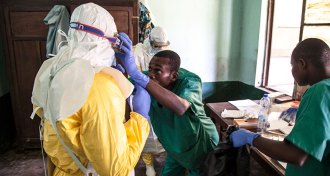 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know about the Ebola outbreak, and the vaccine that might help
Even as an experimental vaccine arrives in Congo to contain the virus, there are worrisome signs Ebola has spread to a city.
-
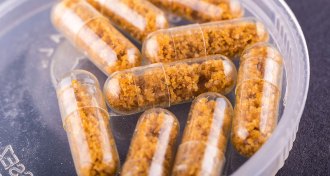 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo regulate fecal transplants, FDA has to first answer a serious question: What is poop?
Fecal transplants are the treatment of the future for some conditions. But right now, they are entirely unregulated. Here’s why putting regulations in place is so complex.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC advises: Don’t swallow the water in a hotel swimming pool
In a 15-year period, hotel swimming pools and water parks had the highest number of swimming-related disease outbreaks in the United States.
By Kyle Plantz -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient Chinese farmers sowed literal seeds of change in Southeast Asia
Two waves of ancient migration from China to Southeast Asia spread farming and languages.
By Bruce Bower