Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologySharp stones found in India signal surprisingly early toolmaking advances
Toolmaking revolution reached what’s now India before Homo sapiens did, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBabies’ kicks in the womb are good for their bones
A new study adds to the evidence that fetal workouts are important for strong bodies.
-
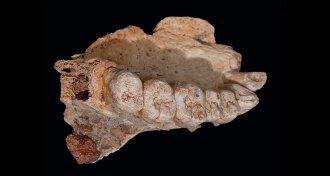 Anthropology
AnthropologyAn ancient jaw pushes humans’ African departure back in time
If an ancient jaw found in an Israeli cave belongs to Homo sapiens, the humans left Africa tens of thousands of years earlier than we thought.
By Bruce Bower -
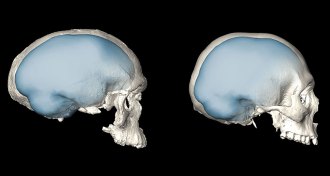 Anthropology
AnthropologyHuman brains rounded into shape over 200,000 years or more
Ancient humans’ brains slowly but surely became round, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Cosmology
CosmologyReaders wonder about the universe’s expansion and more
Readers had questions about the universe's accelerating expansion, a hidden void in the Great Pyramid of Giza and what happens to human waste in space.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsBaby macaques are the first primates to be cloned like Dolly the Sheep
Scientists have cloned two baby macaque monkeys with the same technique used to clone Dolly. The research could help advance the cloning of other species.
By Dan Garisto -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s the key ingredient that lets a centipede’s bite take down prey
A newly identified “spooky toxin” launches a broad attack but might be eased with a version of a known drug.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘First Face of America’ explores how humans reached the New World
New documentary shows how an ancient teen and an infant have illuminated scientists’ understanding of the peopling of the Americas.
By Bruce Bower -
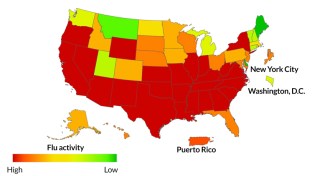 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew twist on a flu vaccine revs up the body’s army of virus killers
A new approach to flu vaccine development makes influenza virus extra sensitive to a powerful antiviral system.
-
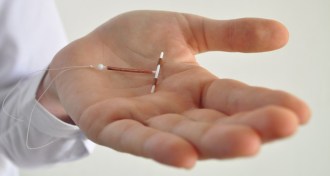 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, IUDs were deemed safe and effective
50 year ago, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declared intrauterine devices safe and effective, though officials didn’t know how the IUDs worked.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHunter-gatherer lifestyle could help explain superior ability to ID smells
Hunter-gatherers in the forests of the Malay Peninsula prove more adept at naming smells than their rice-farming neighbors, possibly because of their foraging culture.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEvidence grows that normal childbirth takes longer than we thought
Another study finds that labor lasts longer than is traditionally taught — an insight that could mean fewer unnecessary cesarean deliveries.