Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEven brain images can be biased
Brain scan studies that are drawn from rich and well-educated groups could lead to biased ideas of how our brains develop.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAn abundance of toys can curb kids’ creativity and focus
Too many toys may lead to more shallow play for toddlers, a new study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking linked to low birth weight in Pennsylvania babies
Babies born to moms living within one kilometer of a hydraulic fracturing site were more likely to be born underweight, researchers say.
-
 Humans
HumansThe story of humans’ origins got a revision in 2017
Human evolution may have involved the gradual assembly of scattered skeletal traits, fossils of Homo naledi and other species show.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWorries grow that climate change will quietly steal nutrients from major food crops
Studies show that rice, wheat and other staples could lose proteins and minerals, putting more people at risk of hunger worldwide.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineApproval of gene therapies for two blood cancers led to an ‘explosion of interest’ in 2017
The first gene therapies approved in the United States are treating patients with certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains of former football players showed how common traumatic brain injuries might be
Examinations of NFL players’ postmortem brains turned up chronic traumatic encephalopathy in 99 percent of samples in large dataset.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika cases are down, but researchers prepare for the virus’s return
The number of Zika cases in the Western Hemisphere have dropped this year, but the need for basic scientific and public health research of the virus remains strong.
-
 Health & Medicine
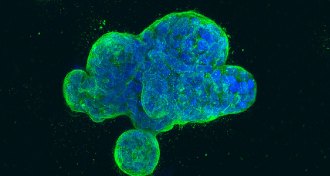
Health & MedicineWhen tumors fuse with blood vessels, clumps of breast cancer cells can spread
Breast cancer tumors may merge with blood vessels to help the cancer spread.
-
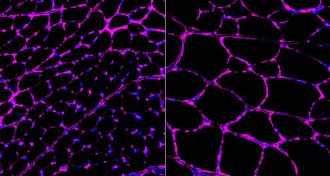 Genetics
GeneticsCRISPR/Cas9 can reverse multiple diseases in mice
A new gene therapy uses CRISPR/Cas9 to turn on dormant genes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat hospitals can do to help keep excess opioids out of communities
Guidelines for prescribing opioids following a routine surgery prevented thousands of unnecessary pills from leaving the hospital, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaring into a baby’s eyes puts her brain waves and yours in sync
Brain waves line up when adults and babies lock eyes.