Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
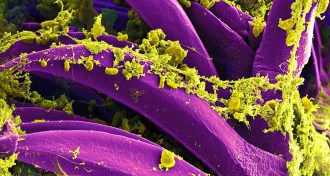
Health & MedicineGenetic tweak turned plague bacterium deadly
Two genetic changes allowed plague bacteria to cause deadly lung infections and pandemic disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes proving to be a danger to teens
E-cigarettes have surpassed cigarettes as the most commonly used tobacco product among teenagers. Medical researchers are sounding the alarm.
By Janet Raloff -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyNo matter the language, disease risk is hard to communicate
Reassuring messages about MERS might seem designed to stop panic. But in reality, people need to hear the truth, even if it’s uncertain.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyMusic to just about everyone’s ears
Common elements of music worldwide point to its central role in group cohesion.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShould you eat your baby’s placenta?
More women are choosing to eat their baby’s placenta after giving birth, but the evidence for benefits isn’t there yet.
-
 Plants
PlantsPoppy yields the final secret to making morphine
Scientists have successfully transplanted most of the morphine synthesis pathway from poppies to yeast. Now the final step is ready to be put in place.
-
 Health & Medicine
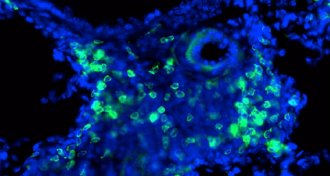
Health & MedicineSwitching off nerve cells eases asthma attacks
A drug that numbs nerve cells in mice’s airways offers a new way to ease the effects of an asthma attack.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
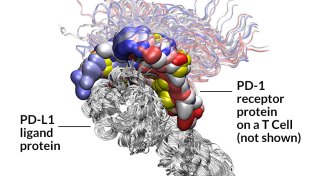
Health & MedicineNew cancer drugs wake up sleeping killer T cells
The immune system’s T cells, often evaded by tumors, might now resume the attack.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyThe guilty pleasure of funny cat videos
Many people love posting and looking at cute kitty content online. A new survey shows that this could be because it helps us manage our emotions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpit test could provide early warning of head, neck cancers
A new study shows that signs of head and neck cancer can be detected in saliva and blood plasma even before tumors are clinically diagnosed.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen baboons travel, majority rules
GPS study suggests baboons use simple rules to resolve travel disputes without leaders.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyKennewick Man’s DNA links him to present-day Native Americans
Genetic analysis of Kennewick Man suggests that the ancient Pacific Northwest man was most closely related to modern Native Americans, not Polynesians.
By Bruce Bower