Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResveratrol’s anticancer benefits show up in low doses
Small amounts of the compound found in red wine and grapes prove protective against colon cancer in mice fed a high-fat diet.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRemains of Jamestown leaders discovered
Colonial-era graves reveal leading figures in founding of English America.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAutism’s journey from shadows to light
Science writer Steve Silberman considers autism in the modern era of neurodiversity - a movement to respect neurological differences as natural human variation - framing the relatively progressive autistic experience of today against the the conditions oppressed past.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBystanders deliver on CPR
People suffering from cardiac arrest are more likely to survive without brain damage if a bystander performs CPR, new studies suggest.
By Nathan Seppa -
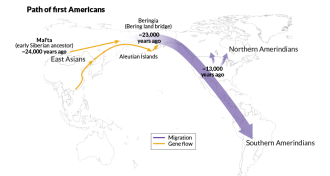 Genetics
GeneticsResearch teams duel over Native American origins
Genetic link between Australia and the Amazon fuels two interpretations of Native American origins.
-
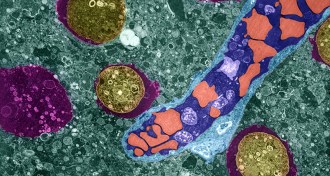 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDeath by brain-eating amoeba is an inside job
Immune response to brain-eating amoeba may be the real killer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBreakdown of Alzheimer’s protein slows with age
It takes longer to get rid of an Alzheimer’s-associated protein with age.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe weekly grind of social jetlag could be a weighty issue
Even those of us with nine-to-five jobs don’t always respect our body’s clocks. Research shows that even slight disruptions might be associated with obesity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMosquitoes can get a double dose of malaria
Carrying malaria may make mosquitoes more susceptible to infection with a second strain of the parasite that causes the disease.
-
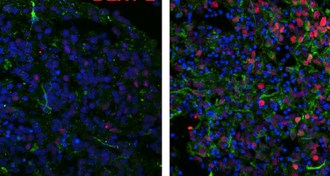 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBundles of cells hint at biological differences of autistic brains
Using miniature organoids that mimic the human brain, scientists have identified developmental differences between autistic children and their non-autistic family members.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn children, a sense of time starts early
Minutes, hours, days and years start to take on new meaning as children acquire a deeper concept of time.
-
 Life
LifeShifted waking hours may pave the way to shifting metabolism
Shift workers are at higher risk for obesity and metabolic problems. Scientists are working hard to understand why the night shift makes our hormones go awry.