Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeThe origin of biological clocks
Most of Earth’s creatures keep time with the planet’s day/night cycle. Scientists are still debating how and why the circadian clocks that govern biological timekeeping evolved.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTooth, jaw fossils tell tale of North America’s last nonhuman primates
Oregon fossils provide new clues to North America’s last nonhuman primates.
By Bruce Bower -
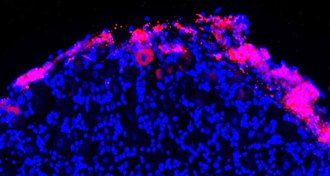 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePotential pain treatment’s mechanism deciphered
Scientists have new insight as to how a class of environment-sensing bone marrow cells can help safely relieve pain.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHow English became science’s lingua franca
A new book explores the roles of war, politics and economics in the rise of English in scientific communication.
-
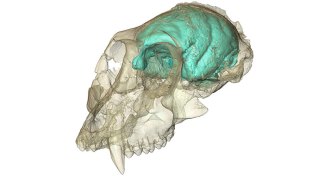 Anthropology
AnthropologyMonkey’s small brain shows surprising folds
An ancient monkey’s tiny brain developed folds, raising questions about primate evolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeWomen blush when ovulating, and it doesn’t matter a bit
Women don’t signal their fertility in obvious ways like nonhuman primates. A new study shows that even skin flushes are too subtle to detect.
-
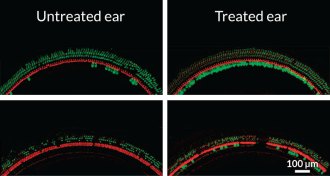 Genetics
GeneticsGene therapy restores hearing in mice
Scientists have used gene therapy to restore hearing in deaf mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew cases of Ebola emerge in Liberia
Liberia has recorded three new Ebola cases after being declared free of the disease in May.
-
 Life
LifeAge isn’t just a number
Getting old happens faster for some, and the reason may be in the blood.
-
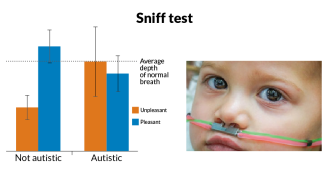 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSmell test may detect autism
A quick sniff test could reveal whether or not a child has autism, but some scientists have doubts.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarette reports provide science that society craves
Research on vaping fills a crucial need in science’s service to society: providing the best information possible in a timely manner, so people can make wise choices.
By Eva Emerson -
 Life
LifePuzzling cosmic signals, processed food defined and more reader feedback
Readers sort out a definition for processed food, discuss the benefits of tinkering with human DNA and more.