CDC panel gives thumbs up to vaccine against nine HPV types
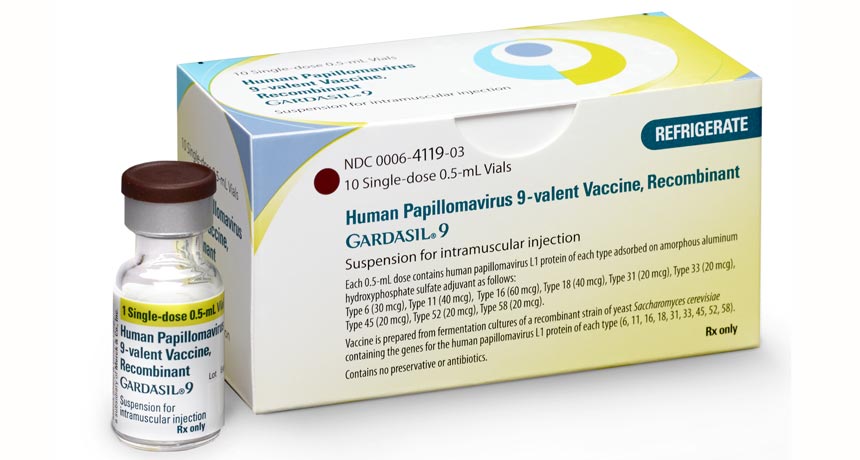
Gardasil 9, a vaccine that offers protection against nine types of HPV, has been recommended for use in 11- and 12-year-old girls and boys and in females ages 13 to 26 and males ages 13 to 21 who have not previously been vaccinated or treated with the three-dose series.
Business Wire