Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-

-
 Life
LifeTest drug stops Marburg virus in monkeys
Using a nano-size piece of RNA, scientists have stopped Marburg virus in monkeys.
-
 Health & Medicine
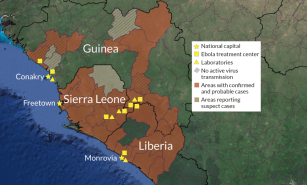
Health & MedicineExperimental drugs and vaccines poised to take on Ebola
The use of experimental drugs and vaccines against Ebola may turn the tide against an outbreak in Africa that has defied efforts to control it.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsLong before Columbus, seals brought tuberculosis to South America
Evidence from the skeletons of ancient Peruvians shows that seals may have brought tuberculosis across an ocean from Africa.
-
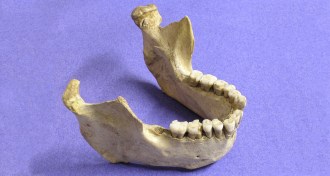 Anthropology
AnthropologyEarlier dates for Neandertal extinction cause a fuss
Revised dates suggest Neandertals coexisted with modern humans for several thousand years in Europe before disappearing 40,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy puts numbers to post-baby sleepiness
Many moms aren’t getting good sleep months after giving birth, reports a new study and every mother ever.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking lab mice back to their roots
Lab mice are incredibly useful for biomedical research. But they are also incredibly inbred. A new study shows that bringing wild mouse traits back could help uncover new links between genes and behavior.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEvidence-based medicine actually isn’t
Demands for evidence-based medicine confront the contradiction that much of the evidence is worthless or skewed.
-
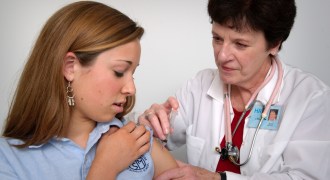 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHPV vaccine protection lasts at least eight years
Immunization shields children from human papillomavirus infection for nearly a decade.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyOrigins of Egyptian mummy making may predate pyramids
Preservative mixture for mummy wrapping found on linens that covered the dead as early as 6,300 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentFetuses may be exposed to antimicrobial compounds
Health risks remain uncertain as scientists find common soap chemicals in pregnant women and cord blood.
By Beth Mole -
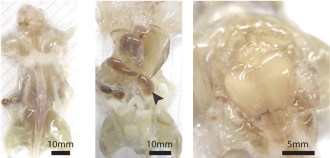 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClearing up anatomy with a see-through mouse
A new method begins with a mouse or rat and ends with a transparent body, where details can be visualized all the way to the DNA. Here’s how it works.