Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInflammation-blocking cells might fight often-fatal sepsis
Treatment saved young and old mice from overactive immune response to infection.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineData deluge feeds paranoia parenting
There are several gadgets and devices you can buy that will feed you reams of data about your baby. But it’s not always clear how that data translate into useful information.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineElderly benefit from high-dose flu shot
High-dose vaccine may offer people age 65 and older improved protection against the flu.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProsthesis uses swinging arms to tell legs when to step
Device creates artificial neural connection that could help paralyzed people walk.
-
 Life
LifeAnimal source of Ebola outbreak eludes scientists
Researchers are trying to determine whether bats or bush meat transmitted the Ebola virus to people in West Africa.
-
 Life
LifeGrizzly bears master healthy obesity
Tuned insulin signals explain how grizzly bears can fatten up for hibernation in the winter without developing diabetes.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
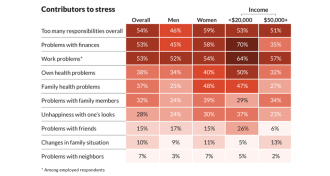
Health & MedicineSurvey catalogs what is stressing out Americans
Along with work and other responsibilities, health problems are prominent causes of stress.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMusic soothes the aging brain in film ‘Alive Inside’
A social worker highlighted in a new documentary goes on a quest to bring tunes to nursing homes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRat moms’ behavior reflected in their babies’ brains
Grooming, nursing and other maternal behaviors cause brain signal changes in offspring, a study in rats finds.
-

-
 Psychology
PsychologyBilingual homes may give babies a learning lift
Hearing two languages during the first six months of life linked to an early mental advantage.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
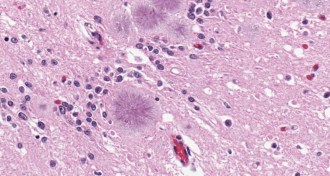
Health & MedicineNew tests screen for lethal prion disease
Urine and nasal swabs can detect small amounts of the abnormal prions that cause Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
By Nsikan Akpan