Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental herpes drug outperforms first-line med
An experimental treatment for genital herpes suppresses the viral infection better than the standard drug, but animal tests raise concerns about side effects.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClinical trial reanalyses may alter who should get treated
Reanalyses of clinical trial data sometimes lead to different treatment suggestions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe (almost non-existent) science of potty training
When it comes to toilet training your child, science will offer you almost no help whatsoever.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesSpeedy test could improve treatment of urinary tract infections
A new test for drug-resistant bacteria may speed the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsArtifacts, fossils tell story of changes to Egypt’s animals
Ancient Egyptian artifacts and fossils from the Nile Valley show a correlation between species extinctions and a growing human population in a drying climate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineViruses can zoom through workplaces in hours
A virus on an office door handle can spread to more than half the people working there within a few hours.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInjectable flu drug could add to weapons against infection
The experimental drug, given in a single shot, could prove useful in the event of a lethal flu pandemic.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPyramid builders could have used rolling blocks
Instead of sliding blocks on a ramp, ancient Egyptians could have rolled the massive bricks to the pyramids, a physicist suggests.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAutism treatment for babies shows promise in small study
A small study finds that changing how parents interact with infants may reduce autism symptoms.
-
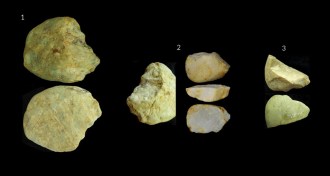 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMore signs emerge of New World settlers before 20,000 years ago
Controversial stone tools of pre-Clovis humans have been excavated in South America.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo-part vaccine protects monkeys from Ebola
An experimental vaccine protected macaques from infection with the Ebola virus up to 10 months after receiving the two-shot regimen.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsMolecular biologist honors ancient bones
After deciphering an ancient skeleton’s genetic secrets, molecular biologist Sarah Anzick helped reinter the remains.