Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists suspected that lost sense of smell could be restored
Cells responsible for humans’ sense of smell can regenerate. Now, research spurred on by the pandemic could help answer questions about the process.
By Aina Abell -
 Health & Medicine
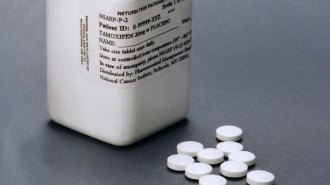
Health & MedicineWhy a popular breast cancer drug may be less effective for some Africans
A genetic variant commonly found in certain African populations appears to impair tamoxifen’s ability to tackle breast cancer.
-
 Life
LifeBonobos, like humans, cooperate with unrelated members of other groups
Cooperation between unrelated individuals in different groups without clear and immediate benefit was thought to be uniquely human. Its presence in bonobos may help explain its evolution.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFlint grapples with the mental health fallout from the water disaster
The water crisis started almost a decade ago. Residents of Flint, Mich., are still healing from the disaster — and caring for their own.
-
 Health & Medicine
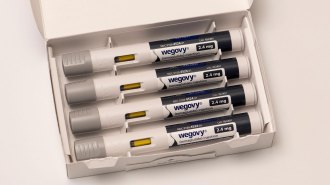
Health & MedicineThe weight-loss drug Wegovy lowered heart attack risk in a large trial
Among 17,000 adults, those on semaglutide were less likely to experience nonfatal heart attacks and strokes or death due to cardiovascular disease.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
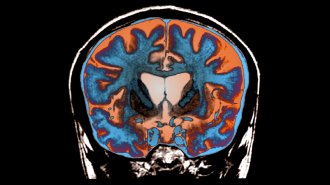
Health & MedicineWhy Huntington’s disease may take so long to develop
Repeated bits of the disease-causing gene pile up in some brain cells. New treatments could involve stopping the additions.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesEvolutionary virologist Daniel Blanco-Melo seeks out ancient pathogens
Daniel Blanco-Melo has reconstructed two viral strains brought to the Americas with European colonizers in the 16th century.
By Pratik Pawar -
 Psychology
PsychologyWhy scientists are expanding the definition of loneliness
Feeling detached from animals, places and routines can cause loneliness, researchers are learning, which may expand the list of interventions.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC is expanding its disease surveillance of international travelers
Passengers at four major U.S. airports will now be tested for over 30 pathogens through a mix of wastewater testing and voluntary nasal swabs.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow neutron imaging uncovers hidden secrets of fossils and artifacts
The technique can complement X-ray scanning and other tools to uncover details of dinosaur fossils, mummies and more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain tissue may be fuel for marathon runners
Myelin, fatty tissue that insulates nerve cells in the brain, may be a renewable energy source for marathon runners and other endurance athletes.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologySurprisingly long-lived wild female chimps go through menopause
Chimpanzees in Uganda are the first known example of wild, nonhuman primates experiencing the hormonal changes, raising questions about how menopause evolved.
By Bruce Bower