Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHe made beer that’s also a vaccine. Now controversy is brewing
An NIH scientist’s maverick approach reveals legal, ethical, moral, scientific and social challenges to developing potentially life-saving vaccines.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis newfound cascade of events may explain some female gut pain
Gut problems like irritable bowel syndrome are often worse in women. A mouse study reveals a pain pathway involving estrogen, gut cells and bacteria.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyAs gambling addiction spreads, one scientist’s work reveals timely insights
Psychiatrist Robert Custer spent his life convincing doctors that compulsive gambling was not an impulse control problem. Today, his research is foundational for diagnosis and treatment.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePolar plunges aren’t just for the daring
Bragging rights and an adrenaline rush aren’t the only reasons to start the year with a frigid swim. A dip in icy water builds resilience.
-
 Humans
Humans‘Black Religion in the Madhouse’ examines psychiatry and race post-Civil War
In the aftermath of slavery, white psychiatrists diagnosed Black people with “religious excitement” and claimed they were unfit for freedom.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBats might be the next bird flu wild card
Finding that vampire bats along Peru’s coast carried H5N1 antibodies raises concerns that multiple bat species could become reservoirs for the virus.
By Jane Qiu -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertals mastered fire-making tools 400,000 years ago
Archaeologists found flint, iron pyrite to strike it and sediments where a fire was probably built several times at an ancient site in England.
By Jay Bennett -
 Psychology
PsychologySome irritability is normal. Here’s when it’s not
Irritability is a normal response to frustrations, but it can sometimes signal an underlying mental health disorder, like depression or anxiety.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGLP-1 drugs failed to slow Alzheimer’s in two big clinical trials
Tantalizing results from small trials and anecdotes raised hopes that drugs like Ozempic could help. Despite setbacks, researchers aren’t giving up yet.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDrought may have doomed the ‘hobbits’ of Flores
Stalagmite data suggest Homo floresiensis faced prolonged drought that stressed both them and their prey, contributing to their disappearance.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA CDC panel has struck down universal newborn hepatitis B vaccination
A reshaped vaccine committee voted to scale back newborn hepatitis B shots despite decades of data showing the birth dose is safe, effective and vital.
-
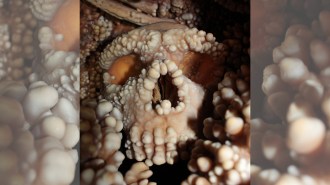 Anthropology
AnthropologyBig Neandertal noses weren’t made for cold
Tiny cameras threaded inside a Neandertal skull provide evidence that their big noses were not an adaptation to cold climates.
By Tom Metcalfe