Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep deprivation hits some brain areas hard
Brain scan study reveals hodgepodge effects of sleep deprivation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsStudy ranks Greenland shark as longest-lived vertebrate
Radiocarbon in eye lenses suggests mysterious Greenland sharks might live for almost 400 years.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsSneaky virus helps plants multiply, creating more hosts
Plant virus makes hosts more attractive to pollinators, ensuring future virus-susceptible plants.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMix of brain training, physical therapy can help paralyzed patients
Long-term training with brain-machine interface helps people paralyzed by spinal cord injuries regain some feeling and function.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsColugo genome reveals gliders as primate cousins
New genetic analysis suggests gliding mammals called colugos are actually sisters to modern primates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsColugo genome reveals gliders as primate cousins
New genetic analysis suggests gliding mammals called colugos are actually sisters to modern primates.
-
 Earth
EarthGeneral relativity has readers feeling upside down
Readers respond to the June 25, 2016, issue of Science News with questions on Earth's age, moaning whales, plate tectonics and more.
-
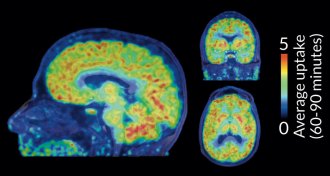 Genetics
GeneticsScientists get a glimpse of chemical tagging in live brains
For the first time scientists can see where molecular tags known as epigenetic marks are placed in the brain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists get a glimpse of chemical tagging in live brains
For the first time scientists can see where molecular tags known as epigenetic marks are placed in the brain.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHumans may have taken different path into Americas than thought
An ice-free corridor through the North American Arctic may have been too barren to support the first human migrations into the New World.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyT. rex look-alike unearthed in Patagonia
A new dinosaur species discovered in Patagonia has the runty forearms of a Tyrannosaurus rex, but is not closely related to the gigantic predator.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsBetty the crow may not have invented her hook-bending tool trick
Textbook example of Betty the crow’s proposed insight into toolmaking is now called into question by observations of similar hook bending by wild New Caledonian birds.
By Susan Milius