Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA viral gene drive could offer a new approach to fighting herpes
A new gene drive can copy and paste itself into the genomes of herpes simplex viruses in mice. The end goal is a version that disables the virus in humans.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
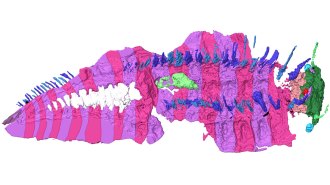
PaleontologyThe largest arthropod to ever live finally has a head
Fossils of an extinct giant millipede reveal new details about the arthropod’s anatomy.
By Jason Bittel -
 Chemistry
ChemistryWork on protein structure and design wins the 2024 chemistry Nobel
David Baker figured out how to build entirely new proteins. Demis Hassabis and John Jumper developed an AI tool to predict protein structures.
By Meghan Rosen and Andrea Tamayo -
 Animals
AnimalsTo tell a right-trunked elephant from a lefty, check the wrinkles
Elephant trunks, more sci-fi face-tentacle than ho-hum mammal nose, are getting new scrutiny as researchers explore how the wrinkles grow.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSemaglutide saps mice’s motivation to run
Mice given semaglutide, the key ingredient in drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy, lost weight, but they also voluntarily ran less on a wheel.
-
 Animals
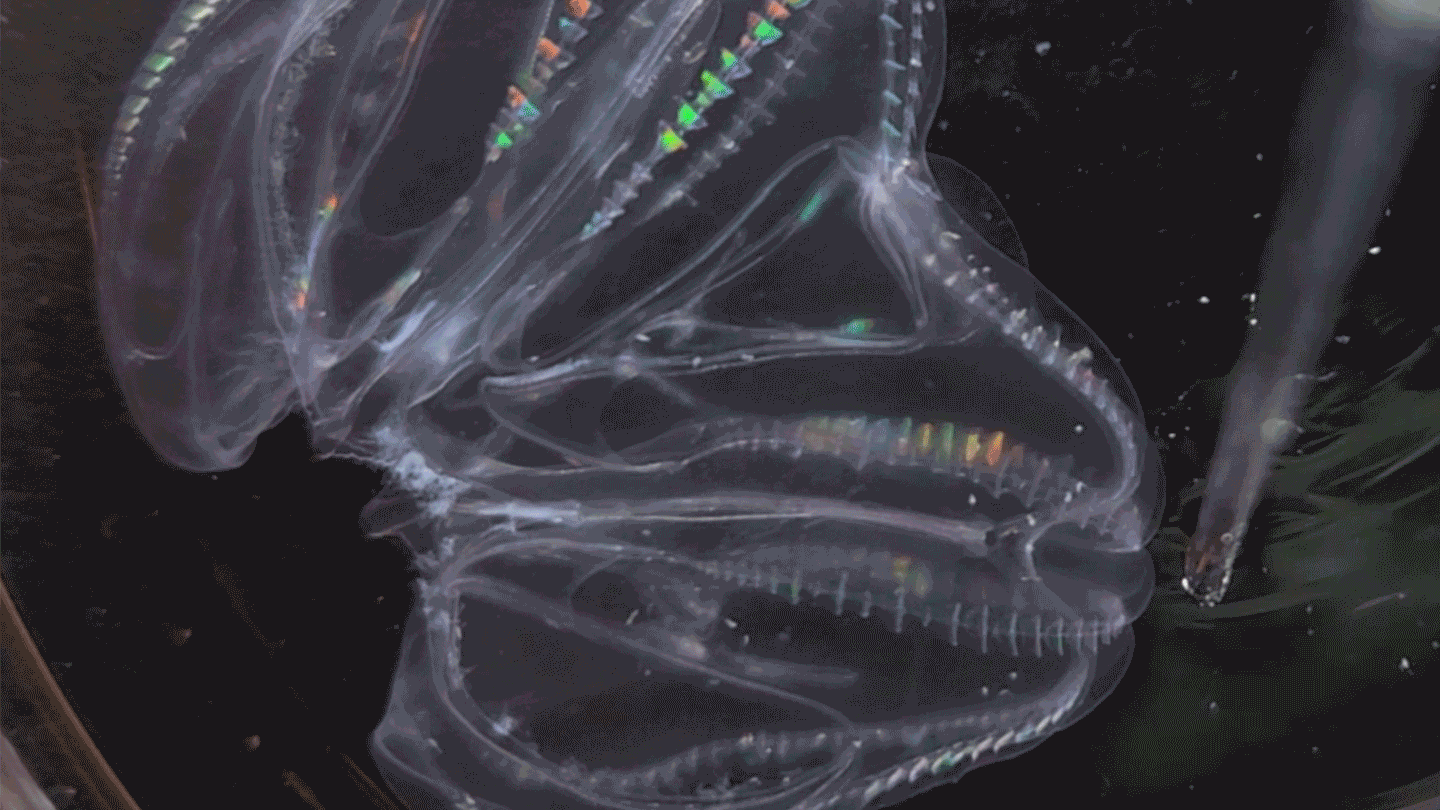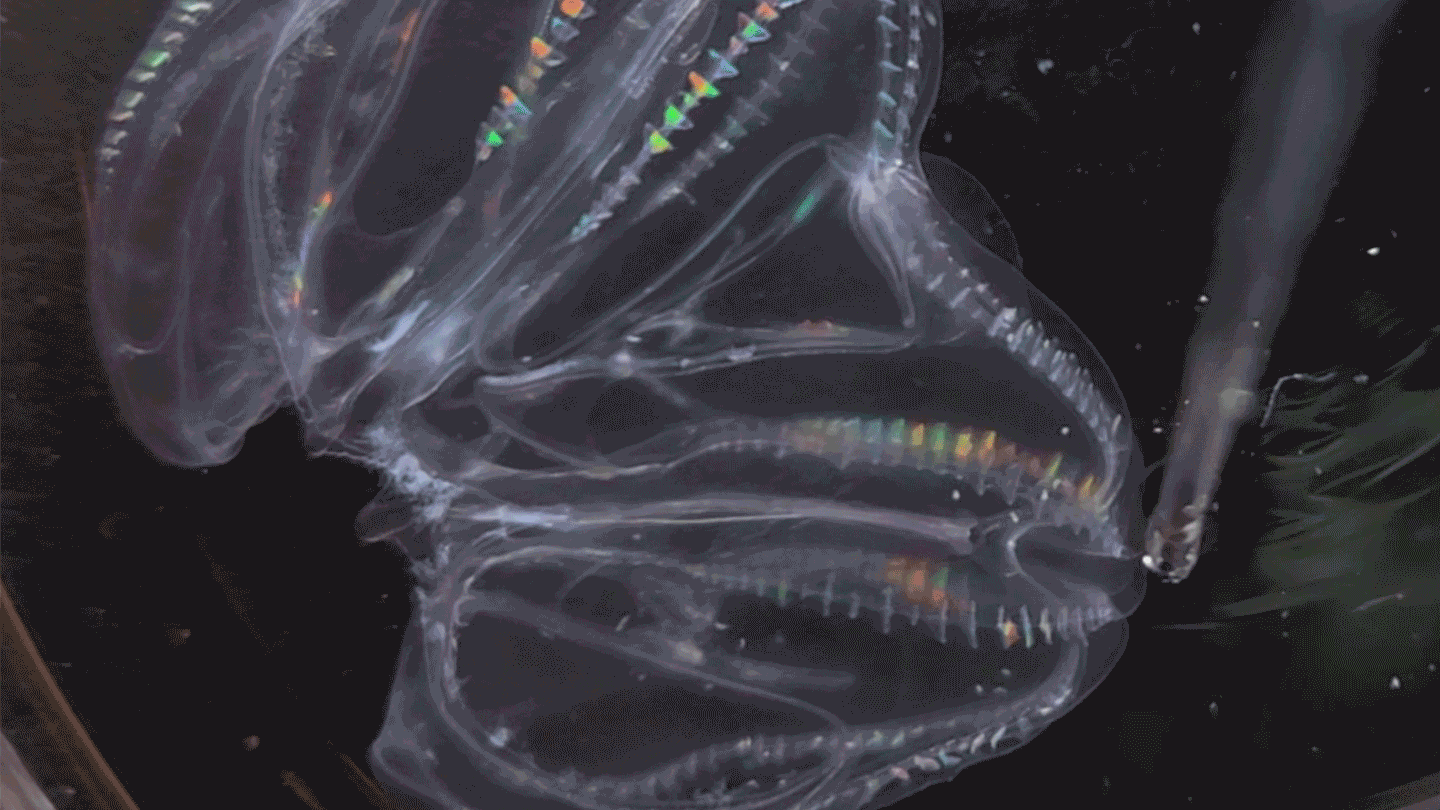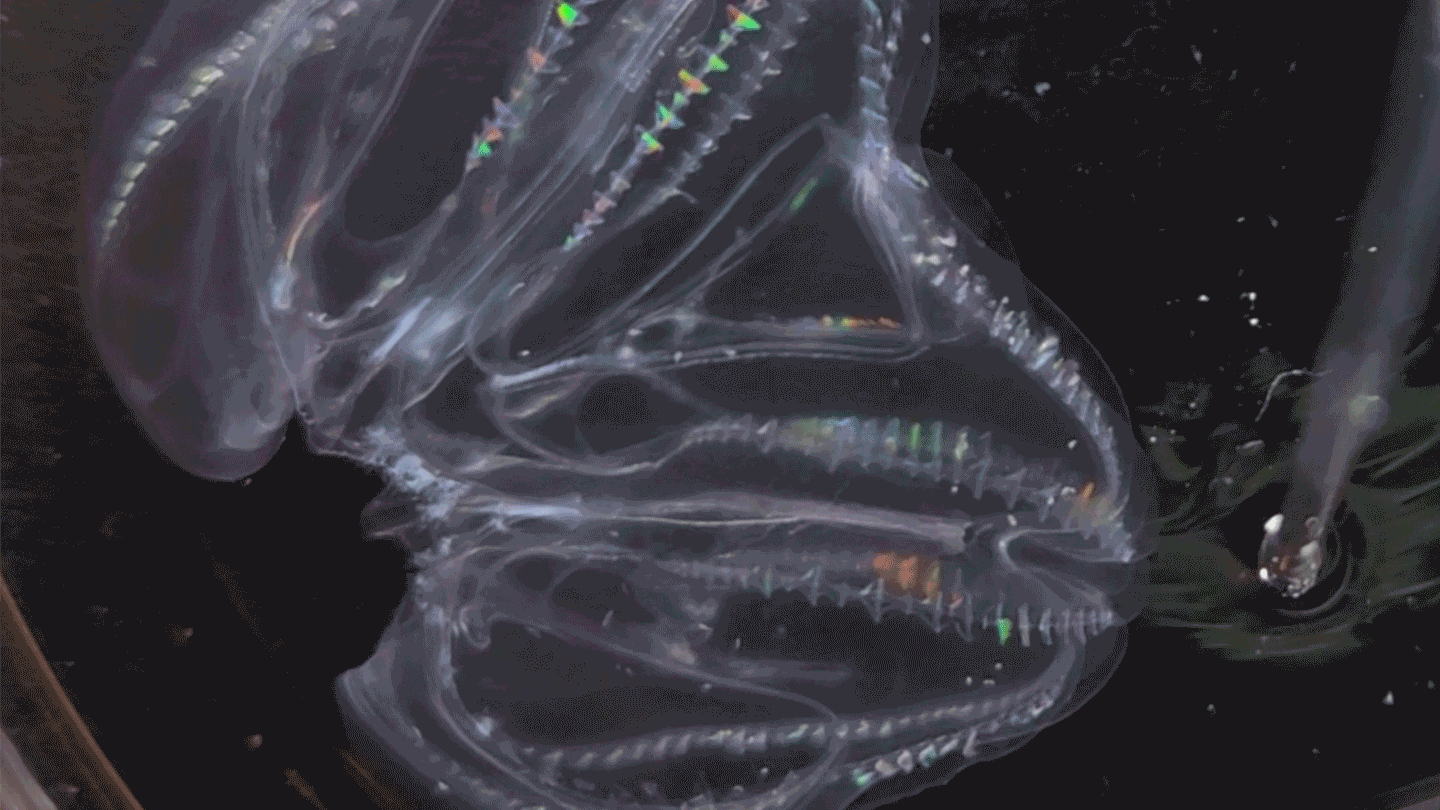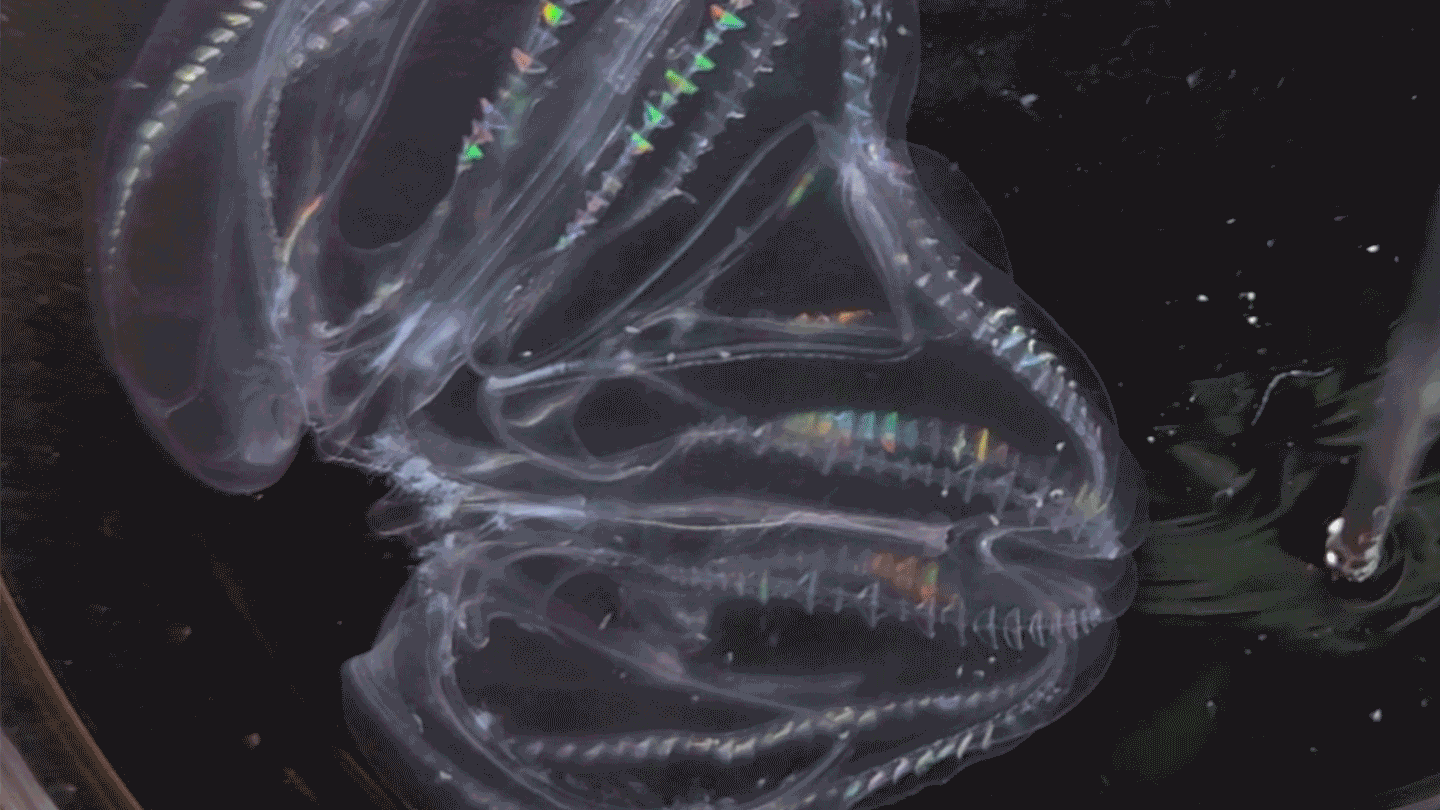
AnimalsThese sea creatures can fuse their bodies
A species of comb jelly can fuse its body with another jelly after injury. Some of the pair’s body functions then synchronize.
By Jude Coleman -
 Genetics
GeneticsThe discovery of microRNA wins the 2024 physiology Nobel Prize
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun found a new principle of gene regulation essential for all multicellular organisms.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Sophie Hartley -
 Animals
AnimalsSome tadpoles don’t poop for weeks. That keeps their pools clean
Eiffinger’s tree frog babies store their solid waste in an intestinal pouch, releasing less ammonia into their watery cribs than other frog species.
-
 Health & Medicine
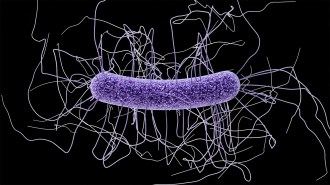
Health & MedicineAn mRNA vaccine protected mice against deadly intestinal C. difficile bacteria
An mRNA vaccine that targets several aspects of C. difficile’s ability to cause severe disease prevented major symptoms and death in mice.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceScientists have traced all 54.5 million connections in a fruit fly’s brain
By tracing every single connection between nerve cells in a single fruit fly’s brain, scientists have created the “connectome,” a tool that could help reveal how brains work.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins’ open-mouth behaviors during play are like smiles, a study claims
Experts urge caution in calling bottlenosed dolphins’ gesture a humanlike “smile,” but agree it seems to be important for how the animals communicate.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCoyotes have the face muscles for that ‘sad-puppy’ look
The ability to make heart-melting stares may not be the fruit of dog domestication if their still-wild cousins have the power to do it too.
By Susan Milius