All Stories
-
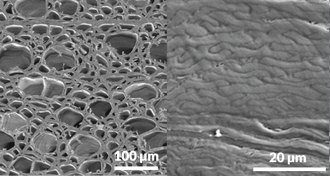 Materials Science
Materials ScienceSuperdense wood is lightweight, but strong as steel
New superdense wood could be a more lightweight, environmentally friendly alternative to current construction materials.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHumans are overloading the world’s freshwater bodies with phosphorus
Human activities are driving phosphorus levels in the world’s lakes and other freshwater bodies to a critical point.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists are tracking how the flu moves through a college campus
Researchers are following the spread of viruses and illness among students in a cluster of University of Maryland dorms to learn more about how the bugs infect.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIt’s a bad idea for a toad to swallow a bombardier beetle
Toads are tough. But there are some insects even they shouldn’t swallow.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomySpaceX just launched its biggest rocket for the first time
SpaceX just launched the Falcon Heavy — the most powerful rocket since the Saturn V — for the first time.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis ancient creature looks like a spider with a tail
A newly discovered ancient creature looks like a spider and has silk spinners and spidery male sex organs.
By Susan Milius -
 Psychology
PsychologyWhen it’s playtime, many kids prefer reality over fantasy
Given a choice between fantasy play and doing the things that adults do, children prefer reality-based tasks, studies suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient kids’ toys have been hiding in the archaeological record
Some unusual finds from thousands of years ago are actually toys and children’s attempts at mimicking adult craftwork.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsPollinators are usually safe from a Venus flytrap
A first-ever look at what pollinates the carnivorous Venus flytrap finds little overlap between pollinators and prey.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyThe way dwarf galaxies move puts a new spin on galaxy formation
Distant dwarf galaxies orbit a larger galaxy in a coordinated loop, rather than randomly as expected. The finding could challenge theories of dark matter.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLaser experiment hints at weird in-between ice
Scientists spot signs of an unusual phase of water called superionic ice.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySome of TRAPPIST-1’s planets could have life-friendly atmospheres
The seven planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1 are probably rocky and some may have life-friendly atmospheres, two new papers suggest.