All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor dwarf mongooses, handstands aren’t just good fun
Dwarf mongooses may use marks laid down in handstand positions to gather information on rivals, a new study shows.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySuper-Earths are not a good place for plate tectonics
The intense pressures inside super-Earths make plate tectonics less likely, new research suggests.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentOil-munching microbes cleaning up Gulf marshes faster than expected
Microbes in some of Louisiana’s marshes are breaking down oil from the Deepwater Horizon spill faster than expected.
By Beth Mole -
 Astronomy
AstronomyAdvice to a baby planet: Avoid black holes
A dust cloud looping around the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole might have once been an infant planet.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyX-ray rings reveal neutron star’s distance
Concentric X-ray rings around a neutron star help astronomers triangulate the star’s distance.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShould you eat your baby’s placenta?
More women are choosing to eat their baby’s placenta after giving birth, but the evidence for benefits isn’t there yet.
-
 Plants
PlantsPoppy yields the final secret to making morphine
Scientists have successfully transplanted most of the morphine synthesis pathway from poppies to yeast. Now the final step is ready to be put in place.
-
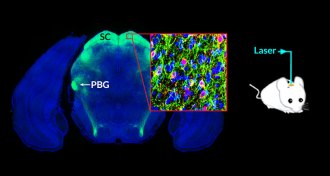 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOne path that fear takes in the brain discovered
By hijacking a newly discovered pathway in mice’s brains, scientists inspire fear.
-
Tiny tweaks helped flu strains thwart 2014-2015 vaccine
Changes to the flu strains circulating around the Northern Hemisphere explain why last year’s flu vaccine didn’t work so well.
By Meghan Rosen -
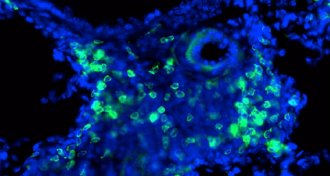 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSwitching off nerve cells eases asthma attacks
A drug that numbs nerve cells in mice’s airways offers a new way to ease the effects of an asthma attack.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary Science50 years ago, Mariner 4 sent back first pictures from Mars
On July 14, 1965, Mariner 4 became the first spacecraft to fly by Mars. The probe also sent back the first pictures of another planet taken from space.
-
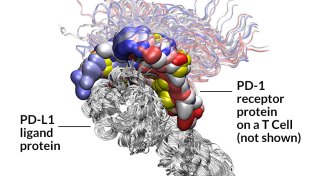 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew cancer drugs wake up sleeping killer T cells
The immune system’s T cells, often evaded by tumors, might now resume the attack.
By Nathan Seppa