All Stories
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFracking chemicals can alter mouse development
Hormone-disrupting chemicals used in fracking fluid cause developmental changes in mice, new experiments show.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePerformance gains from Tommy John surgery still up for debate
Major league baseball pitchers who undergo two Tommy John surgeries have shorter careers than peers who don’t have the surgery, a new study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
Astronomy‘Supernova sweeping’ cleans up a galaxy’s gas
Supernovas might sweep the remaining gas out of a galaxy after a supermassive black hole triggers the end of star formation.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhite House unveils strategy against antibiotic resistance
The Obama Administration has launched a long-term plan to curb antibiotic resistance, unveiling incentives and requirements designed to boost surveillance and diagnosis of resistant microbes.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Materials Science
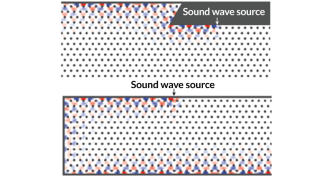
Materials ScienceA new spin on guiding sound waves along a one-way route
A proposed acoustic topological insulator made of an array of spinning metal rods would channel sound waves in one direction along its edge, preventing any sound from bouncing away.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsPanda stalking reveals panda hangouts
Scientists used GPS trackers to learn about the giant panda lifestyle.
-
 Life
LifeBright bird plumage resulted from natural, sexual selection
Darwin hypothesized that bird color differences resulted from sexual selection. Wallace disagreed. A study shows that both were right after all.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceSuds turn silver nanoparticles in clothes into duds
Bleach-containing detergents destroy antibacterial silver nanoparticles that coat clothes.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOur taste in music may age out of harmony
Age-related hearing loss may be more than just the highest notes. The brain may also lose the ability to tell consonance from dissonance, a new study shows.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyEnigmatic 17th century nova wasn’t a nova at all
A nova observed in 1670 was actually two stars colliding, new evidence suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor bats, simple traffic patterns limit collisions
Humans aren’t the only ones who follow traffic rules. Bats do it too, researchers report.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEbola virus not mutating as quickly as thought
The virus causing the current Ebola epidemic in West Africa is not evolving as quickly as some scientists had suggested.