News
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome harlequin frogs — presumed extinct — have been rediscovered
Colorful harlequin frogs were among the hardest hit amphibians during a fungal pandemic. Some species are now making a comeback.
By Freda Kreier -
 Humans
HumansThis ancient Canaanite comb is engraved with a plea against lice
The Canaanite comb bears the earliest known instance of a complete sentence written in a phonetic alphabet, researchers say.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
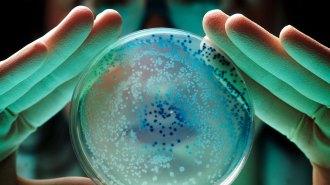
Health & MedicineHere’s how mysterious last-resort antibiotics kill bacteria
Scientists are finally getting a grip on how a class of last-resort antibiotics works — the drugs kill bacteria by crystallizing their membranes.
By Elise Cutts -
 Life
LifeVideo reveals that springtails are tiny acrobats
Poppy seed–sized cousins of insects, famed for wild escape leaping, right themselves in mid-falls faster than cats.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthCatastrophic solar storms may not explain shadows of radiation in trees
Tree rings record six known Miyake events — spikes in global radiation levels in the past. The sun, as long presumed, might not be the sole culprit.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Astronomy
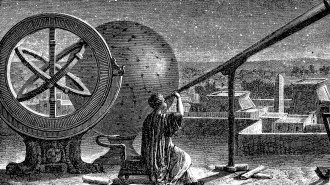
AstronomyPart of a lost, ancient star catalog has now been found
Greek astronomer Hipparchus may be the first to try to precisely map the stars. His lost work turned up on parchment that had been erased and reused.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers have found the closest known black hole to Earth
Discovered by how it pushes around a companion star, the black hole is about 1,500 light-years away and roughly 10 times the mass of the sun.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCat allergies may be tamed by adding an asthma therapy to allergy shots
Adding an antibody already used to treat asthma to standard allergy shots improved cat allergy symptoms for a least a year, a small study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe U.S.’s alcohol-induced death rate rose sharply in the pandemic’s first year
Studies suggested cases of alcoholic liver disease rose in the first pandemic year, and new data show the death rate from alcohol use climbed too.
-
 Physics
PhysicsCrowdsourced cell phone data could keep bridges safe and strong
Accelerometers and GPS sensors in smartphones could provide frequent, real-time data on bridge vibrations, and alert engineers to changes in integrity
-
 Planetary Science
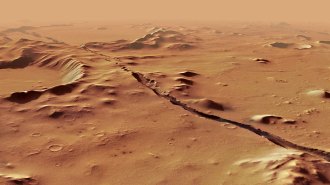
Planetary ScienceMarsquakes hint that the planet might be volcanically active after all
Seismic data recorded by NASA’s InSight lander suggest molten rock moves tens of kilometers below the planet’s fractured Cerberus Fossae region.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDeer-vehicle collisions spike when daylight saving time ends
In the week after much of the United States turns the clock back, scientists found a 16 percent increase in crashes between vehicles and deer.