News
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMammoths may have gone extinct much earlier than DNA suggests
Ancient DNA in sediments may be leading paleontologists astray in attempts to figure out when woolly mammoths and woolly rhinos died out, a new study argues.
By Bas den Hond -
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists explain how to execute a nearly splashless dive
A pocket of air lets elite divers pull off the rip entry, breaking through the water without sending it flying.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDry pet food may be more environmentally friendly than wet food
The environmental cost of wet pet food is higher than dry food, scientists say. That may be because wet food gets most of its calories from animals.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow researchers are working to fill the gaps in long COVID data
Collaboration with patients and with researchers from many specialties is key to better understanding long COVID and managing its many symptoms.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s why some supermassive black holes blaze so brightly
NASA’s IPXE X-ray satellite saw a telltale signature of shock waves propagating along a blazar’s high-speed jet, causing it to emit high-energy light.
-
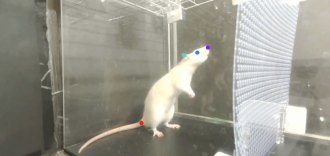 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceRats can bop their heads to the beat
Rats’ rhythmic response to human music doesn’t mean they like to dance, but it may shed light on how brains evolved to perceive rhythm.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA spider monkey’s remains tell a story of ancient diplomacy in the Americas
A 1,700-year-old spider monkey skeleton unearthed at Teotihuacan in Mexico was likely a diplomatic gift from the Maya.
By Freda Kreier -
 Animals
AnimalsLong considered loners, many marsupials may have complex social lives
Some marsupials may be more sociable than previously thought, opening the door to a possible deep legacy of social organization systems in mammals
By Jake Buehler -
 Physics
PhysicsHow physics can improve the urinal
Urinals built with curves like those in nautilus shells eliminate the splash-back common with conventional commodes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePollution mucks up the lungs’ immune defenses over time
A study of immune tissue in the lungs reports that particulate matter buildup from air pollution may impair respiratory immunity in older adults.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese devices use an electric field to scare sharks from fishing hooks
SharkGuard gadgets work by harnessing sharks’ ability to detect electric fields. That could save the animals’ lives, a study suggests.
-
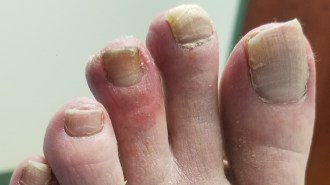 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGot a weird COVID-19 symptom? You’re not alone
From head to COVID toe, doctors have seen a bevy of bizarre cases.
By Meghan Rosen