News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome common medical terms may be more confusing than doctors think
Got ‘bugs in your urine’ or an ‘impressive’ X-ray? Doctors’ jargon can be confusing, especially terms with different everyday and medical meanings.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists thought snakes didn’t have clitorises. They were wrong
Snakes were long thought to be the only reptile group to lack clitorises. But new findings suggest the sex organs are present after all.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthThe Hunga Tonga volcano eruption touched space and spawned a lightning blitz
The eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano in the Pacific Ocean earlier this year was one for the record books — in several surprising ways.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s Perseverance rover captured the sound of a dust devil on Mars
A whirlwind swept over Perseverance while its microphone was on, capturing the sound of dust grains hitting the mic or the NASA rover’s chassis.
By Sid Perkins -
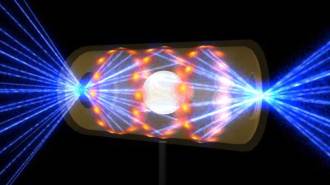 Physics
PhysicsIn a breakthrough experiment, nuclear fusion finally makes more energy than it uses
The sun creates energy through nuclear fusion. Now scientists have too, in a controlled lab experiment, raising hopes for developing clean energy.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyKatydids had the earliest known insect ears 160 million years ago
Fossils from the Jurassic Period show katydid ears looked identical to those of modern katydids and could pick up short-range calls.
-
 Space
SpaceArtemis 1’s Orion capsule returned safely to Earth. What’s next?
The first test flight in NASA’s return to the moon Artemis program ended well with the uncrewed capsule splashing down in the Pacific Ocean.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow much water should you drink a day? It depends on several factors.
A study of more than 5,000 people in 23 countries finds that individual water need varies widely depending on physical and environmental factors.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrief bursts of activity offer health benefits for people who don’t exercise
Non-exercisers who had brief bouts of vigorous day-to-day activity saw a reduced risk of death comparable to that of people who exercise regularly.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHow to make tiny metal snowflakes
In a pool of molten gallium, researchers grew symmetrical, hexagonal zinc nanostructures that resemble natural snowflakes.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Math
MathThe metric system is growing. Here’s what you need to know
Science News spoke with a metrologist about the metric system’s latest update, which will help scientists interpret exceedingly big and small numbers.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA bizarre gamma-ray burst breaks the rules for these cosmic eruptions
The 50-second gamma-ray burst is the first that unambiguously breaks the rule that long bursts usually come from supernovas.