News
-
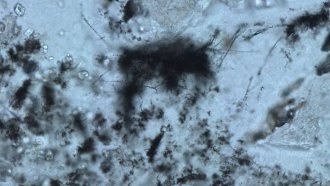 Paleontology
Paleontology3.42-billion-year-old fossil threads may be the oldest known archaea microbes
The structure and chemistry of these ancient cell-like fossils may hint where Earth’s early inhabitants evolved and how they got their energy.
-
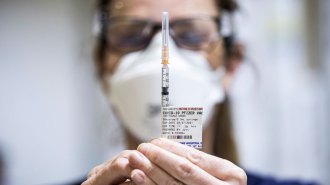 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat experts know so far about COVID-19 boosters for immunocompromised people
Some immunocompromised people remain at risk for severe COVID-19 despite being vaccinated. Studies hint that an additional vaccine dose might help.
-
 Space
SpaceHow do scientists calculate the age of a star?
There are a few different methods to determine the age of a star, but none are perfect.
By Lisa Grossman and Helen Thompson -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA partial skeleton reveals the world’s oldest known shark attack
An ancient shark bite victim died quickly, before his body was recovered and buried, a new study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMarsquakes reveal the Red Planet boasts a liquid core half its diameter
Analyses of seismic waves picked up by NASA’s InSight lander shed new light on the planet’s core and give clues to the thickness of the crust.
By Sid Perkins -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPterosaurs may have been able to fly as soon as they hatched
A fossil analysis shows the flying reptile hatchlings had a stronger bone crucial for lift-off that adults and shorter, broader wings for agility.
-
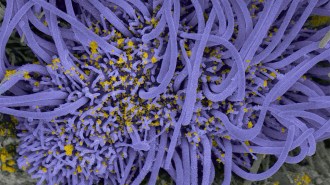 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe coronavirus cuts cells’ hairlike cilia, which may help it invade the lungs
Images show that the coronavirus clears the respiratory tract of hairlike structures called cilia, which keep foreign objects out of the lungs.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has begun its first science campaign
Now about 1 kilometer south of its landing spot, the rover has spotted several promising spots in its search for hints of ancient life.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis butterfly is the first U.S. insect known to go extinct because of people
A 93-year-old Xerces blue specimen’s DNA shows that the butterfly is a distinct species, making it the first U.S. insect humans drove to extinction.
By Jake Buehler -
 Life
LifePikas survive winter using a slower metabolism and, at times, yak poop
Pikas endure bone-chilling temperatures on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau by reducing their metabolism, and when possible, eating yak poop.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe latest picture of a black hole captures Centaurus A’s massive jets
Data from the Event Horizon Telescope reveal new details of jets spewing from the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Centaurus A.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may be leading to overcounts of endangered bonobos
A changing climate in Congo is affecting how scientists count bonobos’ nests, possibly skewing estimates of the great ape population, a study suggests.
By Pratik Pawar