News
-
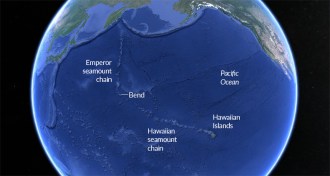 Earth
EarthPlate loss gave chain of Pacific islands and seamounts a bend
The sinking Izanagi tectonic plate may have rerouted the mantle flow beneath the Pacific, halting the Hawaiian hot spot.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominids moved into Greece about 206,000 years ago
New analysis puts people at a contested Greek site about 206,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansEgg-meet-sperm moments are equal opportunities for girls and boys
Despite previous claims, equal numbers of male and female embryos are conceived, new data suggest.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFracking chemicals can alter mouse development
Hormone-disrupting chemicals used in fracking fluid cause developmental changes in mice, new experiments show.
By Beth Mole -
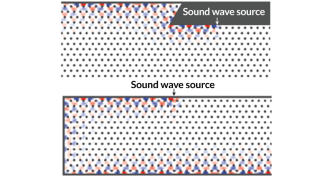 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new spin on guiding sound waves along a one-way route
A proposed acoustic topological insulator made of an array of spinning metal rods would channel sound waves in one direction along its edge, preventing any sound from bouncing away.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeNo-fishing scheme in Great Barrier Reef succeeds with valuable fishes
Coral trout are thriving in marine protected areas in the Great Barrier Reef, but the no-take zones are having a smaller effect on other reef residents, a new 10-year report card shows.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsIceland lays bare its genomes
A detailed genetic portrait of the Icelandic population is helping scientists to identify the genetic underpinnings of disease.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryAir pollution molecules make key immune protein go haywire
Reactive molecules in air pollution derail immune responses in the lung and can trigger life-long asthma.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
AnimalsNeandertal of ant farmers grows modern food
The most old-fashioned fungus-growing ant yet discovered grows a startlingly new-fangled crop.
By Susan Milius -
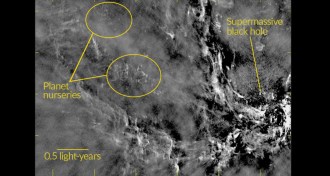 Astronomy
AstronomyUnlikely nursery for new planets is next to massive black hole
Planet nurseries encircle young stars within a few light-years of the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way, scientists claim.
-
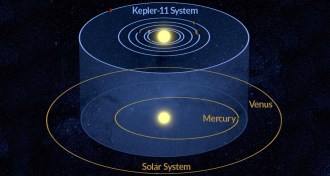 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEarth, neighbors weren’t the first rocky planets in the solar system
Jupiter might have swept an earlier generation of rocky planets into the sun, leaving room for Earth and its neighbors to form.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum links provide clues to causation
Quantum entanglement enables physicists to determine cause and effect just by tracking the association between two measurements.
By Andrew Grant