News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew tests screen for lethal prion disease
Urine and nasal swabs can detect small amounts of the abnormal prions that cause Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceRosetta spacecraft confabs with a comet
After a 10-year chase, ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft has met up with comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySingle black hole may be masquerading as a pair
New observations of a recently discovered binary black hole reveal that astronomers may have been seeing double.
-
 Life
LifeAirborne transmission of Ebola unlikely, monkey study shows
No evidence found of macaque monkeys passing deadly virus to each other.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDebate rages over mouse studies’ relevance to humans
Last year, researchers said rodents are not good mimics of human inflammation; a new study says the reverse.
-
 Astronomy
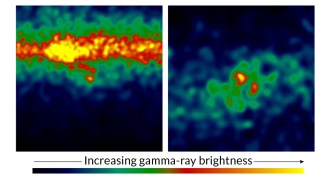
AstronomyGamma rays streaming from stellar explosions stump astronomers
The Fermi satellite detected gamma rays coming from an unexpected source — and astronomers don’t understand what made that possible.
-
 Health & Medicine
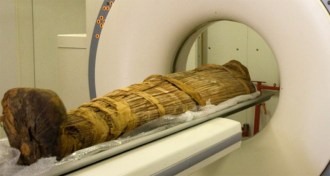
Health & MedicineMummies reveal hardened arteries
Mummy studies suggest heart disease is an ancient malady, not just the product of modern diets and sedentary lifestyles.
-
 Animals
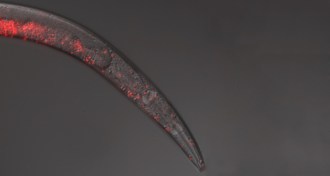
AnimalsNematode sperm go rogue
Worm sperm a killer when nematode species crossbreed.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePart of brain’s pleasure network curbed in mice with chronic pain
Part of brain’s pleasure network is muffled in mice with chronic paw injuries, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResistance to key malaria drug spreads
Parasites that are less susceptible to artemisinin now affect several Asian countries.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaurs shrank continually into birds
Steady miniaturization and rapidly changing skeletons transformed massive animals into today’s fliers.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhen looking for aliens, try finding their pollution
Future telescopes may discover civilized aliens by detecting the industrial pollutants called fluorinated gases in exoplanet atmospheres.