News
-
 Neuroscience
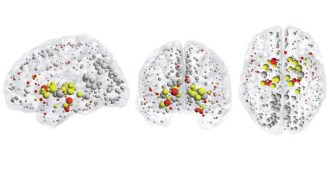
NeuroscienceBusy brain hubs go awry in disorders, study suggests
Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and other brain disorders may occur when the brain’s most active hubs are damaged.
-
 Life
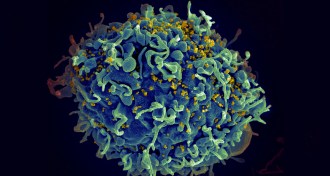
LifeHIV hides in growth-promoting genes
The discovery that HIV can trigger infected cells to divide means scientists may need to rethink strategies for treating the virus that causes AIDS.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHidden heart rhythm problem may underlie some strokes
In two clinical studies, people who had had strokes with no trigger sometimes also had undiagnosed atrial fibrillation.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
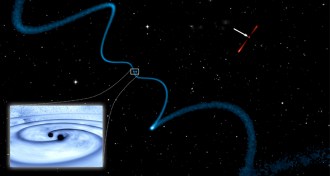
AstronomyRare trio of supermassive black holes found
Three supermassive black holes residing where two distant galaxies collide offer new clues about where to look for gravitational waves.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWeapon inspection scheme would test for nukes but keep designs secret
Technique borrowed from computer science could improve weapon verification and encourage countries to agree to nuclear disarmament.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsLionfish dance can recruit partner for hunting
Slow but superb predators recruit pals for cooperative hunting, often striking in what looks like well-mannered turn taking.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJunk food ahead of pregnancy may harm baby-to-be
Women who have poor diets in the year before conception might have a higher risk of delivering a baby preterm than do women who eat healthful foods
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyGalaxy seed found from 3 billion years after Big Bang
A still-growing core of a galaxy in the early universe may help astronomers understand how massive elliptical galaxies get their start.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassenger pigeon population had booms and busts
DNA says the birds recovered from hard times — until people came along.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeAutoimmune diseases stopped in mice
Reprogramming immune cells may offer a way to treat autoimmune diseases without harming the body’s ability to fight infections.
-
 Humans
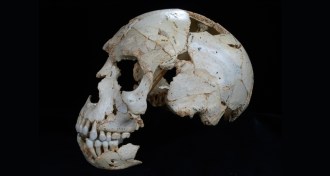
HumansSkulls reveal Neandertal’s hodge-podge genealogy
A new analysis of ancient hominid skulls reveals a patchy anatomical start of the Neandertal lineage.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsCommercial quantum computer fails to impress in new test
Fifteen million dollar D-Wave machine runs no faster than traditional computer in head-to-head challenge.
By Andrew Grant