News
-
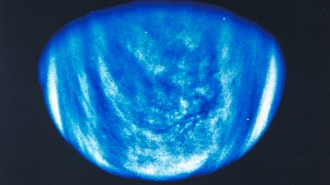 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceA private mission to Venus aims to look for signs of life
If successful, Morning Star would be the first private mission to another planet and the first in over 30 years to directly measure Venus’s clouds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat experts say about childhood vaccines amid the Texas measles outbreak
As the Texas measles outbreak grows and HHS head RFK Jr. puts vaccines under new scrutiny, two experts answer questions about the public health tool.
-
 Tech
TechSquirty gels bring the taste of cake and coffee to virtual reality
By squirting chemicals onto a person’s tongue to taste, a new device aims to replicate food flavors for fuller virtual experiences.
By Simon Makin -
 Astronomy
AstronomySome of Earth’s meteors are probably coming all the way from a neighboring star system
The triple star system is sending comets, asteroids and meteors our way, and the number of interstellar objects entering the solar system will rise.
By Ken Croswell -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMount Vesuvius turned this ancient brain into glass. Here’s how
Transforming the brain tissue to glass would have required an extremely hot and fast-moving ash cloud, lab experiments suggest.
By Alex Viveros -
 Space
SpaceThe International Space Station lacks microbial diversity. Is it too clean?
Hundreds of surface swabs reveal the station lacks microbial diversity, an imbalance that has been linked to health issues in other settings.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMarried men are doing more cleaning and laundry than in the past
Some scholars argue that efforts to equalize the time men and women spend on housework has stalled. An analysis reveals slow progress.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHumans moved into African rainforests at least 150,000 years ago
This oldest known evidence of people living in tropical forests supports an idea that human evolution occurred across Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceAncient Mars wasn’t just wet. It was cold and wet
Mars may once have held enough water to fill oceans and form coastlines. The planet’s red dust contains water and likely formed in cold conditions.
By Skyler Ware -
 Life
LifeA skull found in Egypt shows this top predator stalked ancient Africa
Archaeologists uncovered a fossilized skull of an ancient sharp-toothed predator that likely hunted early elephants and primates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow fish biologists discovered birds of paradise have fluorescent feathers
A survey of museum specimens reveals that more than a dozen species of the birds sport biofluorescence in feathers, skin or even inside their throats.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFired federal workers share the crucial jobs no longer being done
Thousands of probationary federal employees received termination notices. Many were doing crucial work at science-related agencies.
By McKenzie Prillaman and Alex Viveros