Uncategorized
-
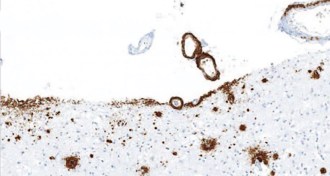 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMisfolded proteins implicated in more brain diseases
Alzheimer’s, other disorders show similarity to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other prion infections.
-
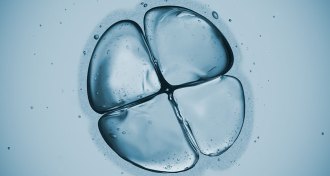 Life
LifeSmall number of genes trigger embryo development
New views of early embryo development reveal differences between humans and mice.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen octopuses dance beak to beak
The larger Pacific striped octopus does sex, motherhood and shrimp pranks like nobody else.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMinutes after encountering danger, lemurs yawn
Madagascar primates yawn within minutes of encountering threats.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
OceansEarth got first whiff of oxygen 3.2 billion years ago
Photosynthesis by early cyanobacteria pumped oxygen into Earth’s oceans 200 million years earlier than once thought, new geochemical analyses show.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarliest sea scorpion discovered in Iowa
Earliest sea scorpion discovered in impact crater in Iowa.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Environment
EnvironmentMolting seals shed mercury along with fur
Seals spew amassed mercury when they shed, creating hotbeds of pollution in otherwise pristine coastal environments.
By Beth Mole -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe sad magnetic state of the solar system’s rocky worlds
While a strong magnetic shield protects Earth from the sun’s occasional outbursts, the solar system’s other rocky planets are mostly defenseless.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNobel laureate finds beauty in science and science in beauty
In ‘A Beautiful Question,’ Frank Wilczek explores links between math and art
-
 Animals
AnimalsA monkey uses a stick to pick its teeth and nose
A wild bearded capuchin monkey in Brazil was caught using tools to pick its nose and teeth.
By Erin Wayman -
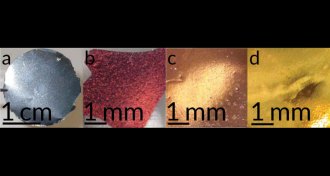 Materials Science
Materials ScienceGraphene shows signs of superconductivity
Ultrathin sheets of carbon can conduct electrical current with no resistance at low temperatures.
By Andrew Grant -
 Environment
EnvironmentLatest BPA replacement seeps into people’s blood and urine
Replacements for BPA called BPS and BPSIP may raise health risks for cashiers.
By Beth Mole