Cosmic dust may create Mars’ wispy clouds
Magnesium from passing comets could be a key part of the Red Planet’s cloud-starter kit
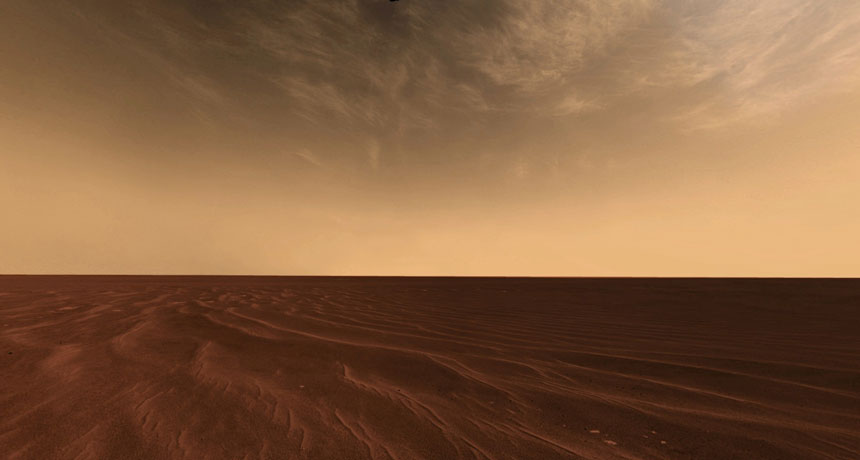

HEAD IN THE CLOUDS The rover Opportunity snapped this picture of wispy clouds drifting through the Martian sky in 2006. New findings suggest the clouds might have condensed around particles of dust from comets.
JPL-NASA, Cornell Univ.