New data fuel debate on universe’s expansion rate
Quasar observations support higher value for Hubble constant
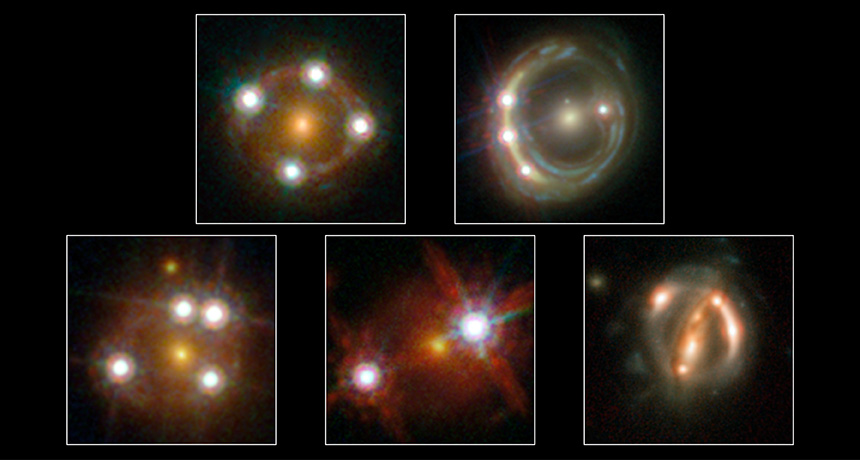

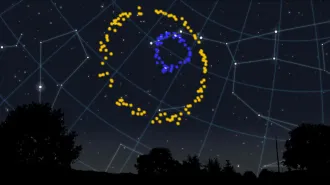
TWINKLING LIGHTS Five quasars, shown, helped scientists make a new measurement of the universe’s expansion rate.
ESA/Hubble, NASA, Suyu et al.