Physics greats of the 20th century mixed science and public service
New biographies highlight Enrico Fermi’s and Richard Garwin’s contributions to science and society.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

There may be ways to block tumors from adapting and outrunning the body’s defenses.
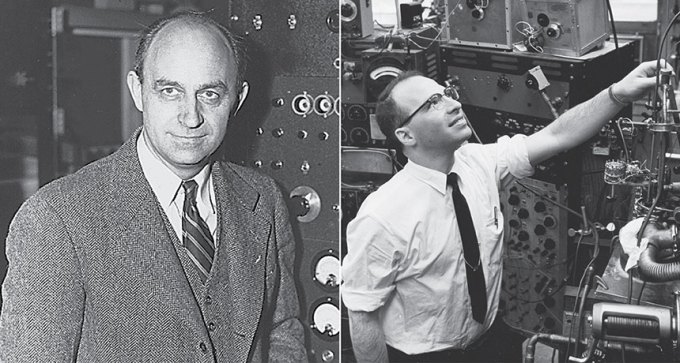
New biographies highlight Enrico Fermi’s and Richard Garwin’s contributions to science and society.
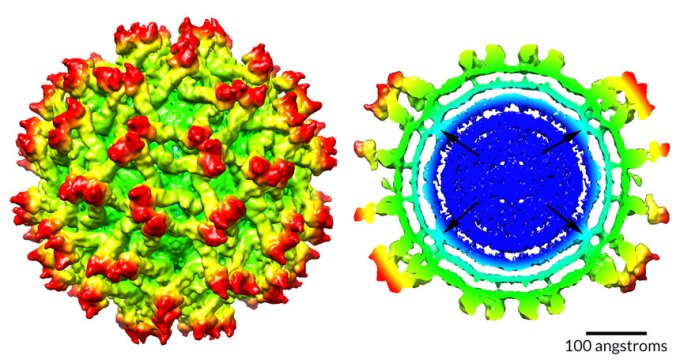
A cryo-electron microscopy map of immature Zika virus offers a never-before-seen glimpse of remodeling of the virus’s protein and RNA core.

New study reveals anatomical secrets of mysterious deep ocean fish.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

Researchers are designing catalysts to move chemical reactions without using precious metals, or at least using less of them.

Increased runoff to the ocean due to climate change could raise neurotoxic mercury in coastal sea life by disrupting the base of the food web.
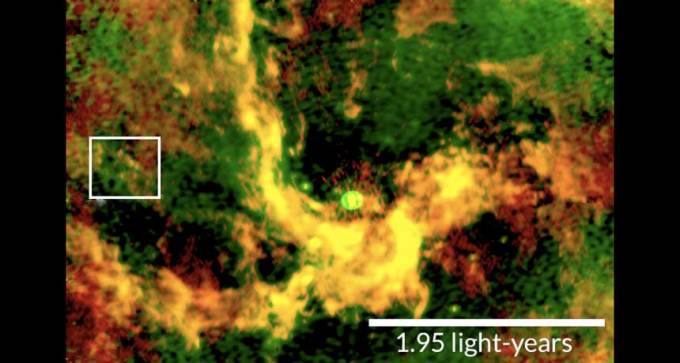
Four clouds of gas near the galactic center have roughly the right mass to be young stars, possibly with planets.

Excess of X-rays could indicate decaying sterile neutrinos.
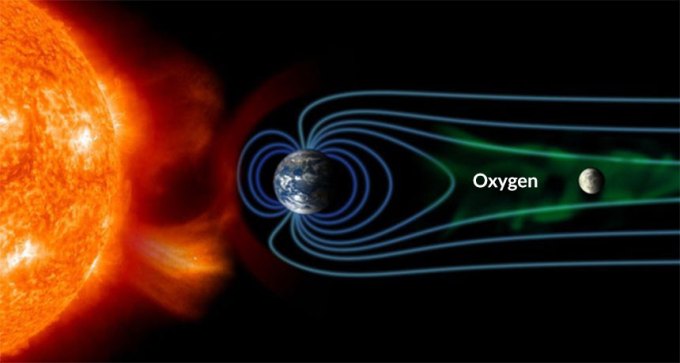
Oxygen atoms originating from the upper atmosphere periodically bombard the moon’s surface, researchers propose.
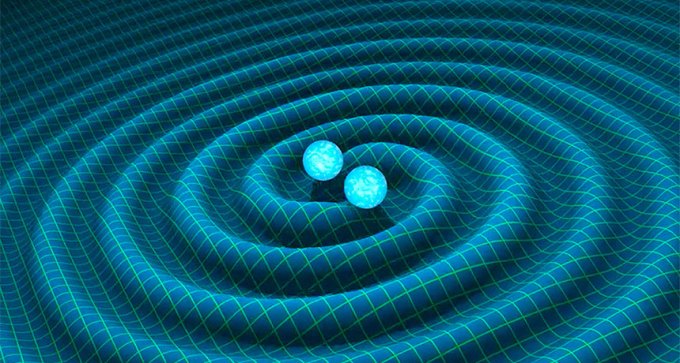
High rate of spin could indicate that black holes formed from previous mergers of black holes.

Zircon crystals from a long-gone continent called Mauritia may have resurfaced during volcanic eruptions on the island of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean.

Wealthy woman’s 2,600-year-old grave highlights Central Europe’s early Iron Age links to Mediterranean societies.
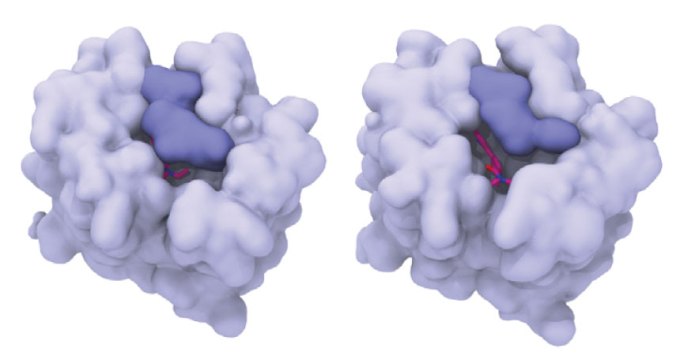
The newly discovered structure of a human serotonin receptor linked to LSD could reveal why the drug’s hallucinogenic effects last so long.

Here’s what puts the grip in a frog’s high-speed strike: quick-change saliva and a tongue softer than a marshmallow.

Updated experiments hope to resolve neutron lifetime discrepancy.
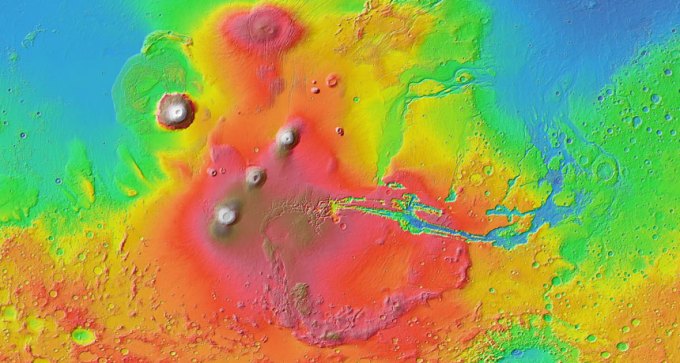
The magma fueling a Martian volcanic system remained largely unchanged for billions of years, analysis of a newfound meteorite suggests.
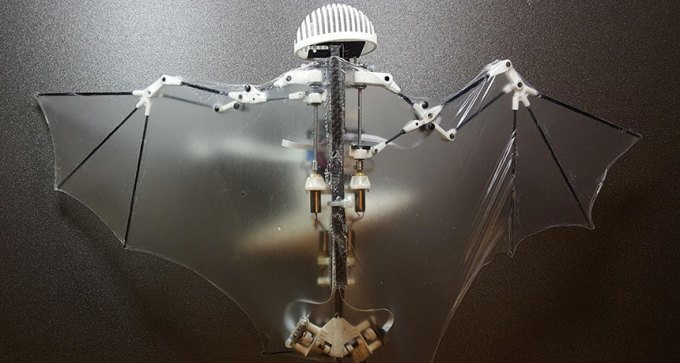
Unlike other aerial robots that use whirling rotor blades to fly, the Bat Bot relies on soft, silicone-based wings to glide, swoop and turn.
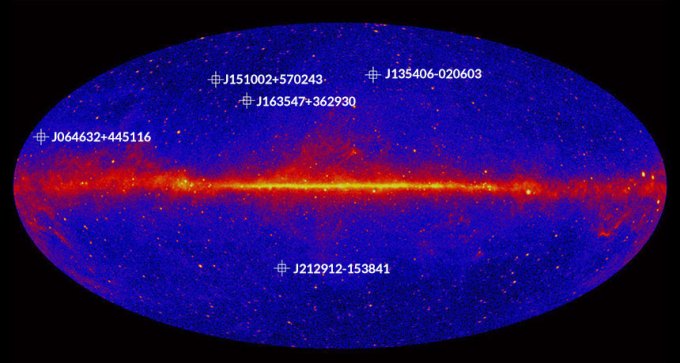
Intensely bright galaxies are the farthest blazars ever detected in gamma rays.

Quasar observations add to discrepancy in measurements of the universe’s expansion speed.
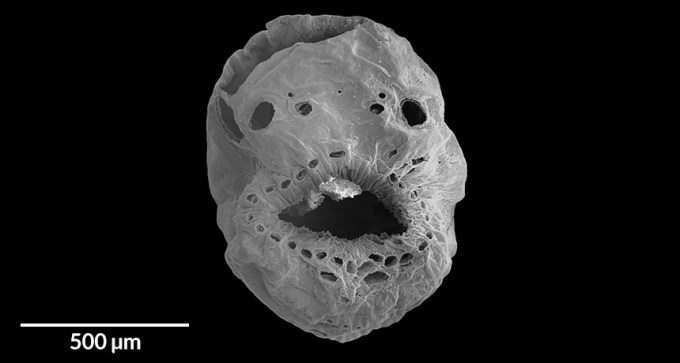
Dozens of tiny fossils discovered in 540-million-year-old limestone represent the earliest known deuterostomes, a diverse group of animals that includes humans and sea cucumbers.

Ancient hunter-gatherers in East Asia are remarkably similar, genetically, to modern people living in the area. Unlike what happened in Western Europe, this region might not have seen waves of farmers take over.

Gravitational lensing has revealed extremely faint galaxies in the early universe, suggesting these tiny galaxies were responsible for cosmic reionization.

The Great Oxidation Event that enabled the eventual evolution of complex life began 100 million years earlier than once thought, new dating of South African rock suggests.

Climate change overheating sea turtle nestlings may be a greater danger than temperature-induced shifts in their sex ratios.
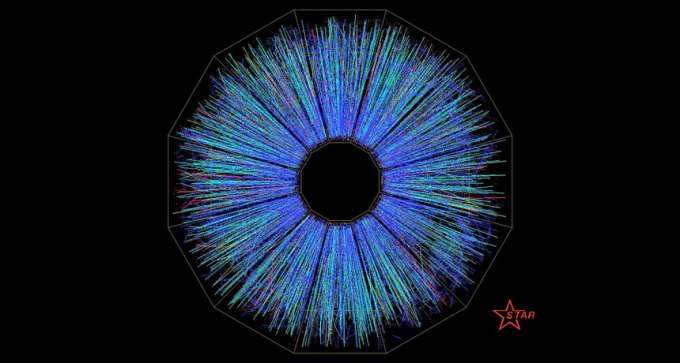
Collisions of gold ions create a fluid with more vorticity than any other known.

Spillback of Zika virus into monkeys may complicate eradication efforts.

Genetic evidence alone may overestimate numbers of species, researchers warn.

A new device uses cold plasma to kill foodborne pathogens.

Mice treated with a blend of antibodies survived even when treated days after exposure to ricin.
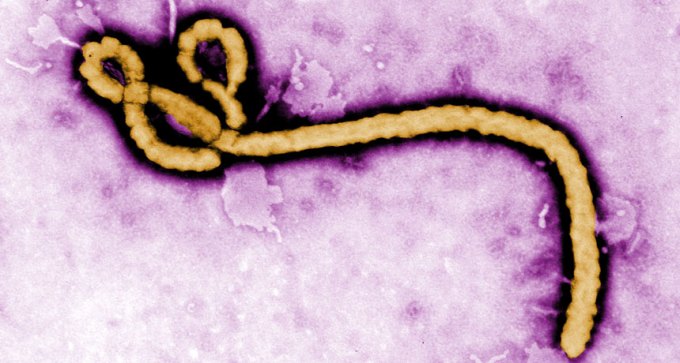
Scientists are developing highly specific antibodies to detect Ebola sooner.

Early versions of computer speech recognition relied on word sounds. Now, they add pattern recognition and a lot of statistics.
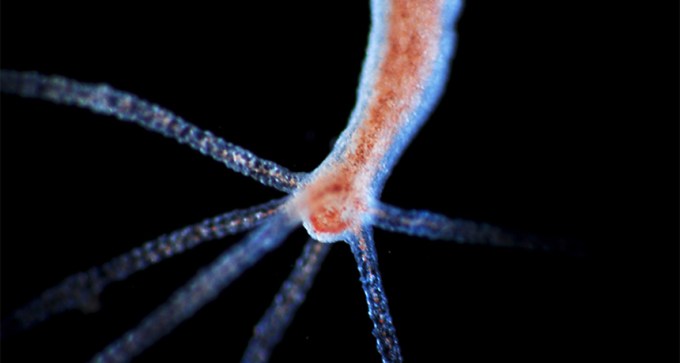
Regenerating pond animals called hydras inherit structural patterns from their original forms, researchers find.

Chinese researchers used a CRISPR/Cas 9 gene editor to make cows more resistant to tuberculosis.

Coconut crabs use their surprisingly powerful claw for more than cracking coconuts.

Deadly cone snails wander in circles and become less capable hunters when exposed to higher levels of carbon dioxide in seawater.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.