Search Results for: GENE THERAPY
Skip to resultsCan’t find what you’re looking for? Visit our FAQ page.
1,057 results for: GENE THERAPY
-
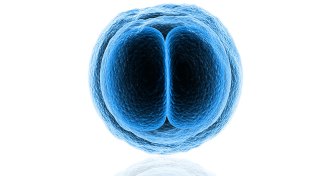 Genetics
GeneticsEditing human germline cells sparks ethics debate
Human gene editing experiments raise scientific and societal questions.
-
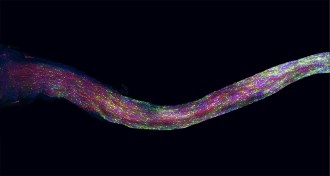 Genetics
Genetics‘Brainbow’ illuminates cellular connections
A mouse’s optic nerve fluoresces in a rainbow of colors. The image offers a detailed look at nerve-protector cells called oligodendrocytes.
-
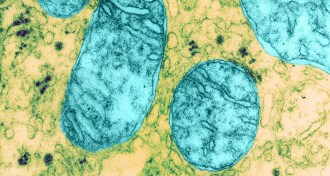 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic editing can delete deleterious mitochondria
A new technique slates mutant mitochondria for destruction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSame mutations can show up in tumors, healthy tissues
Analyzing samples of healthy and tumor tissues could pinpoint which mutations are driving cancer and help develop better-targeted treatments.
By Nathan Seppa -
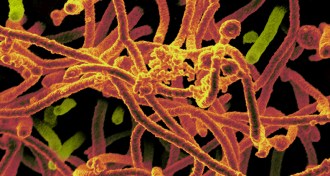 Genetics
GeneticsEbola virus not mutating as quickly as thought
The virus causing the current Ebola epidemic in West Africa is not evolving as quickly as some scientists had suggested.
-
 Life
LifeIn battle to shape immunity, environment often beats genes
The environment, especially microbes, shapes immune system reactions more than genes do.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCompassionate colleagues can help labs restart after disaster
Scientists plan for many things, but often not for disaster. Two scientists share their story of recovery after Superstorm Sandy.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentColorado deluge produced flood of drug-resistance genes
Flooding in Colorado’s South Platte River Basin washed antibiotics and drug-resistance genes into pristine waterways.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes can redeem themselves to fight disease
With some genetic engineering, bacteria can morph from bad to good and help attack invading cancer cells.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMighty muscles may stave off depression
Strong muscles protect the brain from stress-induced toxin associated with depression, a study in mice suggests.
-
 Life
LifeVagina bacteria make molecules that could be drugs
Microbes on the human body are capable of producing thousands of small molecules that hold potential as drugs.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA story about why people get fat may be just that
In this issue, reporters look at efforts to find the genes that could be responsible for the obesity crisis and how evolution acts on diseases such as Ebola and tuberculosis.
By Eva Emerson