Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsBad Karma can ruin palm oil crops
Missing epigenetic mark makes for Bad Karma and poor palm oil crops.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth’s magnetic mystery forces scientists to get creative
In explaining the Earth’s magnetic field paradox, scientists may discover a new question with an even more interesting answer.
By Eva Emerson -
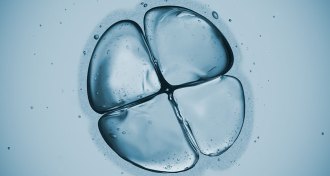 Life
LifeSmall number of genes trigger embryo development
New views of early embryo development reveal differences between humans and mice.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA architecture, novel forensics offer new clues
Going from theory to practice is always rife with problems, be it shifting from the sequence of DNA’s letters to observing its dynamic machinations or from an identity marker in the lab to a piece of courtroom evidence.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood test can predict breast cancer relapse
Blood tests for breast cancer DNA can predict relapse.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe human genome takes shape and shifts over time
Scientists are mapping and modeling the 4-D human genome to get beyond its linear structure.
-
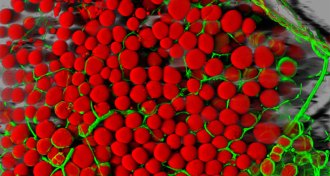 Genetics
GeneticsGene thought to cause obesity works indirectly
Researchers have discovered a “genetic switch” that determines whether people will burn extra calories or save them as fat.
-
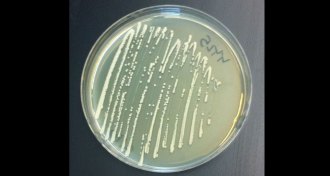 Chemistry
ChemistryPathway pieced together to make opiates in yeast
Scientists have engineered yeast to make sugar into thebaine, a precursor to opiates such as morphine.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow an octopus’s cleverness may have evolved
Scientists have sequenced the octopus genome, revealing molecular similarities to mammals.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncestral humans had more DNA
A new genetic diversity map marks where humans have gained and lost DNA.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow Ethiopian highlanders adapted to breathe thin air
Lower levels of a heart protein may help Ethiopian highlanders breathe thin air, researchers report.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWolves in jackals’ clothing
Africa’s golden jackals are really a species of wolf and deserve a name change, DNA evidence indicates.