Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists perform the first pig-to-human lung transplant
The genetically modified lung remained viable for nine days, but the recipient’s immune responses need more research, scientists say.
By Skyler Ware -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShifting vaccine guidelines inject uncertainty into getting fall COVID shots
Respiratory viruses often surge in the fall. We asked an infectious diseases expert how best to protect ourselves given a shifting vaccine landscape.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinemRNA vaccines hold promise for many diseases. Now the tech is under fire
Researchers warn that halting federal contracts for mRNA vaccine research could weaken pandemic preparedness and slow medical advances.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
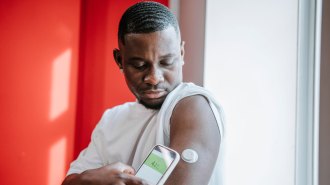
Health & MedicineMeasure blood sugar with a grain of salt
Continuous glucose monitors are now readily available. With guidance, they can help people make small dietary and lifestyle changes for better health.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCould babies get bird flu through breast milk? Maybe, a study hints
H5N1 bird flu might infect human mammary glands, potentially allowing the virus to show up in breast milk.
-
 Humans
HumansThese female divers spend more time underwater than any other humans
At an average age of 70, these women divers in South Korea still forage in the sea up to 10 hours a day and spend more than half of that time underwater.
-
 Humans
HumansStopping menopausal hormones may require more bone monitoring
Women face a small rise in fracture risk within 10 years of stopping therapy, suggesting the need for additional monitoring.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe sugar substitute sucralose makes immunotherapy less effective
Found in Splenda, sucralose reduces immunotherapy efficacy via its effects on the gut microbiome, but arginine supplements might counter the outcome.
By Payal Dhar -
 Health & Medicine
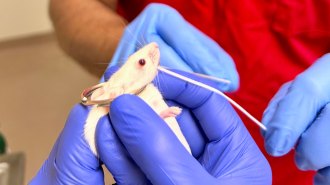
Health & MedicineHow flossing a mouse’s teeth could lead to a new kind of vaccine
Flu viruses often enter the body through mucous tissue in the nose. Researchers are developing new ways to protect such areas.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew clues emerge on how foods spark anaphylaxis
In two studies of mice, a molecule called leukotriene helped trigger food-induced anaphylaxis. A drug approved for asthma — zileuton — diminished it.
- Genetics
This snail may hold a secret to human eye regeneration
Golden apple snails can regrow full, functional eyes. Studying their genes may reveal how to repair human eye injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat is the best exercise to improve sleep?
An analysis of 30 trials delivered a surprising twist: One exercise outperformed walking, resistance training and aerobic exercise in the treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia.
By Kamal Nahas