Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental herpes drug outperforms first-line med
An experimental treatment for genital herpes suppresses the viral infection better than the standard drug, but animal tests raise concerns about side effects.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClinical trial reanalyses may alter who should get treated
Reanalyses of clinical trial data sometimes lead to different treatment suggestions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe (almost non-existent) science of potty training
When it comes to toilet training your child, science will offer you almost no help whatsoever.
-
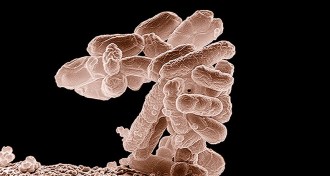 Microbes
MicrobesSpeedy test could improve treatment of urinary tract infections
A new test for drug-resistant bacteria may speed the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineViruses can zoom through workplaces in hours
A virus on an office door handle can spread to more than half the people working there within a few hours.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInjectable flu drug could add to weapons against infection
The experimental drug, given in a single shot, could prove useful in the event of a lethal flu pandemic.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAutism treatment for babies shows promise in small study
A small study finds that changing how parents interact with infants may reduce autism symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo-part vaccine protects monkeys from Ebola
An experimental vaccine protected macaques from infection with the Ebola virus up to 10 months after receiving the two-shot regimen.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTest Ebola treatments to be rushed to West Africa
The World Health Organization has announced that it will use test treatments in West Africa starting this fall.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA story about why people get fat may be just that
In this issue, reporters look at efforts to find the genes that could be responsible for the obesity crisis and how evolution acts on diseases such as Ebola and tuberculosis.
By Eva Emerson -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient famine-fighting genes can’t explain obesity
Scientists question the long-standing notion that adaptation — specifically the evolution of genes that encourage humans to hold on to fat so they can survive times of famine — has driven the obesity crisis.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTrial drug improves heart failure patients’ chance of survival
Novartis’ experimental therapy LCZ696 lowers blood pressure and increases survival rates when compared with a standard drug.
By Nathan Seppa