Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Humans
HumansTextile archaeologists use ancient tools to weave a tapestry of the past
Using tools leftover from ancient spindles and looms, textile archaeologists are starting to understand the fabrics of the past.
By Amber Dance -
 Humans
HumansA historic opioid trial highlights what we know about the deadly drugs
An Oklahoma judge finds that Johnson & Johnson must pay $572 million to the state for the company’s role in the epidemic.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow strep throat may spark OCD and anxiety in some kids
A potential link between strep throat and sudden mental disorders in children raises questions about how infections can alter the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAn Illinois patient’s death may be the first in the U.S. tied to vaping
Officials have announced one death among nearly 200 patients with severe lung illnesses that are potentially related to vaping.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMarijuana and meth are getting more popular in America, but cocaine has declined
In 2006, drug users spent more on cocaine than on heroin, marijuana or methamphetamine. By 2016, marijuana expenditures had exceeded the other drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaping may have sent 153 people to hospitals with severe lung injuries
In the last two months, 16 U.S. states have reported 153 people hospitalized with lung injuries that may be tied to vaping.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHigh blood pressure throughout middle age may increase the risk of dementia
A pattern of high blood pressure during midlife followed by high or low readings in one’s golden years is linked to dementia.
-
 Anthropology
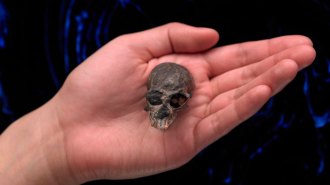
AnthropologyA tiny skull fossil suggests primate brain areas evolved separately
Digital reconstruction of a fossilized primate skull reveals that odor and vision areas developed independently starting 20 million years ago or more.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansIndia’s Skeleton Lake contains the bones of mysterious European migrants
Not all of the hundreds of skeletons found at a north Indian lake are from the same place or period. What killed any of these people is still unknown.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeElectrodes show a glimpse of memories emerging in a brain
Nerve cells in an important memory center in the brain sync their firing and create fast ripples of activity seconds before a recollection resurfaces.
-
 Life
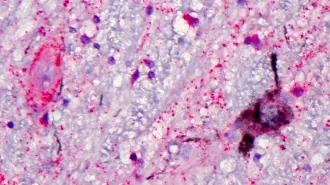
LifeAlzheimer’s targets brain cells that help people stay awake
Nerve cells in the brain that are tied to wakefulness are destroyed in people with Alzheimer’s, a finding that may refocus dementia research.
-
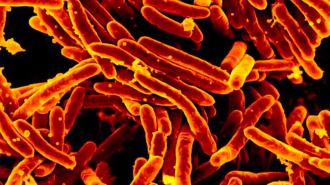 Humans
HumansA new FDA-approved drug takes aim at a deadly form of tuberculosis
The antibiotic could help tackle extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, which kills tens of thousands each year.