Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
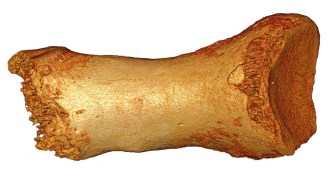
LifeNeandertal genes point to interbreeding, inbreeding
DNA from 50,000 years ago underscores modest levels of mating across hominid populations.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
MicrobesA newfound respect for the microbial world
Despite what many people think about humans’ place in the scheme of things, scientists are finding more evidence that we live in a world of microbes.
By Eva Emerson -

-
 Animals
AnimalsChina trumps Near East for signs of most ancient farm cats
Earliest evidence found for grain as a force in feline domestication.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDog dust may benefit infant immune systems
Microbes from pet-owning houses protected mice against allergy, infection.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyEaster Island’s farmers cultivated social resilience, not collapse
A Polynesian society often presumed to have self-destructed shows signs of having carried on instead.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsYou are what your dad ate, perhaps
Your development is affected by what your mother ate while she was pregnant with you. Is it also affected by what your father ate? A new study suggests that folate deficiency in dads can affect their offspring through epigenetic changes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceConcussion-free head blows may still affect brain
Some college athletes who played contact sports had more changes in their brain’s white matter than varsity competitors in less violent games.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor babies, walking opens a whole new world
Walking and talking are linked as babies develop, anecdote and data show.
-
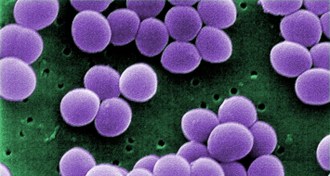 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaph bacteria linger deep in our noses
The nasal cavity has hidden crevices where the disease-causing bacteria like to hang out.
-
 Life
LifeDietary changes affect gut microbes within a day
Menu restricted to meat, egg and cheese alters bacterial mix more than eating only plants.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceNanoglue attaches tissues to each other
Silica particles could repair and help engineer human organs.
By Beth Mole