Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTV linked with brain changes in kids
A new study of Japanese children gives more reasons not to park kids in front of the tube.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCancer vaccine in near future foreseen
Excerpt from the December 21, 1963 issue of SCIENCE NEWS LETTER.
-

-
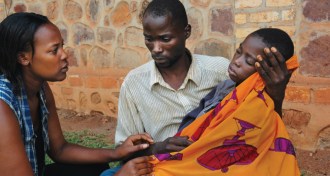 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHeal thy neighbor
As antidepressants and other drugs gradually replace psychotherapy in the United States, new forms of the talking cure are growing in popularity in developing countries ravaged by civil war and poverty.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyGut reaction could foretell marriage satisfaction
Unconscious gut reactions may predict happy, and not-so-happy, marriages, a new study suggests.
-
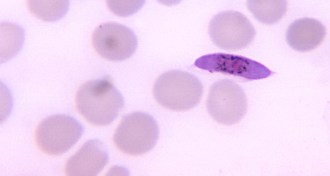 Life
LifeCompounds defeat malaria at every step
Experimental drugs are first to kill all stages of the parasite’s infection cycle.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple dietary supplements could help stave off AIDS
Many people newly infected with HIV stayed healthy on regimen involving multivitamins and selenium.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThalidomide treats Crohn’s disease
Study of children with the inflammatory bowel disorder raises possibility of new use for tainted drug.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChilling body doesn’t stop bacterial infection
Lowering the body temperature of individuals with severe bacterial meningitis may not help to improve patients’ health and could do more harm than good.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStarting exercise late in life still helps with aging
Becoming and staying active as an older individual can lead to a more years without long-term health conditions.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyEarly shrine unearthed at Nepal Buddhist site
Ritual structure could help pin down when the sage known as the Buddha lived in South Asia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople prefer to just get pain over with
A new study shows that people would rather experience pain ASAP, even if it means experiencing more pain.