Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeScientists have a new word for birds stealing animal hair
Dozens of YouTube videos show birds stealing hair from dogs, cats, humans, raccoons and even a porcupine — a behavior rarely documented by scientists.
-
 Health & Medicine
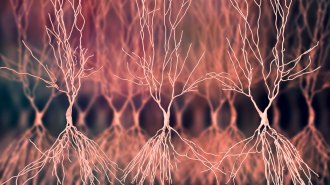
Health & MedicineRipples in rats’ brains tied to memory may also reduce sugar levels
Brain signals called sharp-wave ripples have an unexpected job: influencing the body’s sugar levels, a study in rats suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSquirrels use parkour tricks when leaping from branch to branch
Squirrels navigate through trees by making rapid calculations to balance trade-offs between branch flexibility and the distance between tree limbs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSnake-eating spiders are surprisingly common
Spiders from at least 11 families feed on serpents many times their size, employing a host of tactics to turn even venomous snakes into soup.
By Asher Jones -
 Earth
EarthA new book reveals stories of ancient life written in North America’s rocks
In ‘How the Mountains Grew,’ John Dvorak probes the interlinked geology and biology buried within the rocks of North America.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA hammerhead shark baby boom near Florida hints at a historic nursery
Finding an endangered shark nursery in a vast ocean is like finding a needle in a haystack. But that’s just what scientists did near Miami.
-
 Animals
AnimalsViruses can kill wasp larvae that grow inside infected caterpillars
Proteins found in viruses and some moths can protect caterpillars from parasitoid wasps seeking a living nursery for their eggs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPolar bears sometimes bludgeon walruses to death with stones or ice
Inuit reports of polar bears using tools to kill walruses were historically dismissed as stories, but new research suggests the behavior does occur.
-
 Life
LifeIf confirmed, tubes in 890-million-year-old rock may be the oldest animal fossils
Newly described wormlike fossils may be ancient sea sponges. If confirmed, the fossils would reveal a remarkably early start to animal life.
By Jake Buehler -
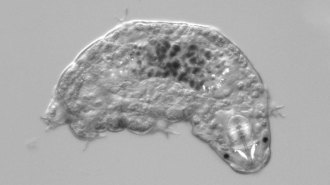 Life
LifeNear-invincible tardigrades may see only in black and white
A genetic analysis suggests that water bears don’t have light-sensing proteins to detect ultraviolet light or color.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow some lizards breathe underwater
Researchers have figured out how some anole lizards can stay underwater for as long as 18 minutes.
-
 Life
Life‘Wild Souls’ explores what we owe animals in a human-dominated world
The new book Wild Souls explores the ethical dilemmas of saving Earth’s endangered animals.