Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
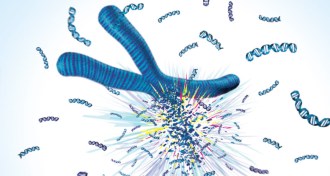
GeneticsThe upside of a demolished chromosome
A woman’s rare genetic disease was cured when a chromosome carrying the mutant gene shattered.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSnail shell creates blue iridescence with mineral
Mollusk shines blue using calcium compound rather than organic molecule.
-
 Life
LifeCyborg beetles reveal secrets of insect flight
Remote controlled beetles swoop to the rescue in insect flight simulations.
-
 Paleontology
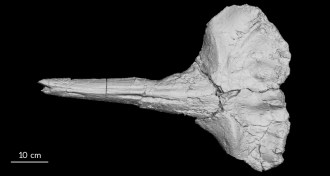
PaleontologyRise of East African Plateau dated by whale fossil
A whale fossil is helping to pinpoint when the East African Plateau started to rise and how the uplift played a role in human evolution, scientists say.
-
 Animals
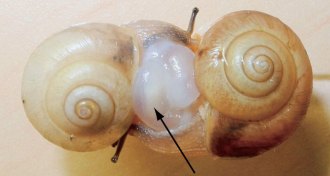
AnimalsGetting stabbed is no fun for land snails
When hermaphroditic land snails mate, they stab each other with “love darts.” But being darted comes at a price, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNanocrystals explain chameleons’ color shifts
Tiny crystals embedded in chameleons’ skin reflect specific wavelengths of light based on their position, explaining how chameleons change colors.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
AnimalsA brain chemical tells when to fight or flee
Crickets tally the knocks they take in a fight, and flee when their brains release nitric oxide to tell them they’ve had enough.
-
 Life
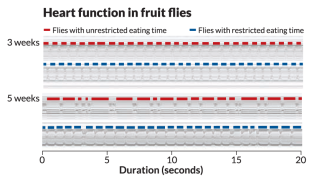
LifeFor healthy eating, timing matters
Limiting eating times improves heart function in fruit flies.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSniffing out human pheromones
A new review argues that most of the chemicals labeled human pheromones, and the experiments behind them, don’t pass the smell test.
-
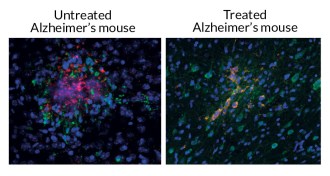 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceUltrasound attacks Alzheimer’s plaques
A new study offers clues to how ultrasound may work as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
-
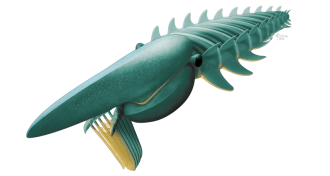 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow arthropods got their legs
New fossils reveal how arthropods evolved branching limbs.
-
 Life
LifeChickens to blame for spread of latest deadly bird flu
Chickens are responsible for the second wave of H7N9 bird flu in China.