Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow species will, or won’t, manage in a warming world
Fast evolution and flexibility, in biology and behavior, may allow some species to adapt to a warming world. Others may need help from humans, or risk dying out.
-
 Life
LifeMicroscapes take off at D.C’s Dulles airport
“Life: Magnified,” a display of microscope images depicting cells, microbes and details of life invisible to the naked eye runs from June to November.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDecline in birds linked to common insecticide
In addition to harming bee populations, neonicotinoid insecticides may also be detrimental to bug-eating birds.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeOcean microbes orchestrate gene activity
The bacteria’s daily cycles aren’t just for photosynthesis, a new study suggests.
-
 Life
LifeFiber optics in mammals’ eyes separate colors
Specialized cells in the retina separate different wavelengths of light to enable sharp vision during the day without harming night vision.
-
 Health & Medicine
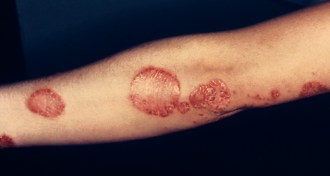
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Life
LifeGecko adhesion takes electric turn
Challenging a favored theory, measurements suggest that electrostatic interactions make gecko feet supersticky.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYet another reason to hate ticks
Ticks are tiny disease-carrying parasites that should also be classified as venomous animals, a new study argues.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDuck-billed dinosaurs roamed the Arctic in herds
Young and old duck-billed dinosaurs lived together in herds in the Arctic, tracks preserved in Alaska indicate.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal largest airborne bird
Despite its massive size, an extinct bird may have been an efficient glider.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMicroplastics lodge in crab gills and guts
Crabs can absorb microplastic particles through their gills and by eating polluted mussels.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsIf you really hate a species, try eating it
Dining on invasive fish such as snakehead and lionfish can reduce their numbers, but we can’t entirely eat our way out this problem.