Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-

-

-
 Animals
AnimalsAnt lions hunt despite sealed lips
Ant lions are ferocious predators, but some of them don’t have a mouth. At least not in the usual sense.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsMysterious neurotoxin may help flatworms kill prey
Tetrodotoxin, the deadly chemical in pufferfish, could help flatworms transform their earthworm prey into puddles of goo.
By Beth Mole -
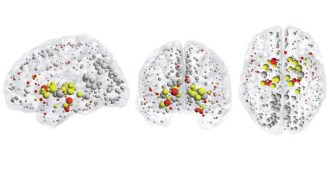 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBusy brain hubs go awry in disorders, study suggests
Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and other brain disorders may occur when the brain’s most active hubs are damaged.
-
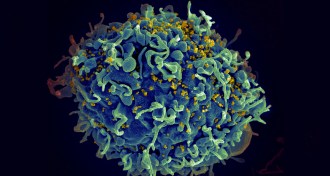 Life
LifeHIV hides in growth-promoting genes
The discovery that HIV can trigger infected cells to divide means scientists may need to rethink strategies for treating the virus that causes AIDS.
-
 Physics
PhysicsTiny silica spheres put the disco in disco clams
The electric effect in disco clams is actually the result of light scattering off tiny silica spheres.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLionfish dance can recruit partner for hunting
Slow but superb predators recruit pals for cooperative hunting, often striking in what looks like well-mannered turn taking.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeLife began when algorithms took control
Digital storage of molecular information is the key to defining life and understanding its origin, astrobiologists say.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThe most personal data on your phone is your microbiome
Phones carry more than your contacts and messages. They’ve got your microbiome too.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny frogs host an illusion on their backs
How dyeing dart frogs move changes how predators see the amphibians, a new study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe simplest form of learning is really quite complex
Habituation, the ability to ignore irrelevant stimuli, is the simplest form of learning but may require a whole neural network.