Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesIrish potato famine microbe traced to Mexico
The pathogen that triggered the Irish potato famine in the 1840s originated in central Mexico, not the Andes, as some studies had suggested.
-
 Oceans
OceansDusk heralds a feeding frenzy in the waters off Oahu
Even dolphins benefit when layers of organisms in the water column overlap for a short period.
-

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain’s support cells play role in hunger
Once considered just helpers for neurons, astrocytes sense the hormone leptin and can change mice’s appetites.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow a genetic quirk makes hair naturally blond
Natural blonds don’t need hair dye. They have a variation on a genetic enhancer that dampens pigment production in their hair follicles, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPets’ rights explored in ‘Citizen Canine’
Science journalist David Grimm describes pet's progression towards full citizenship.
-
-
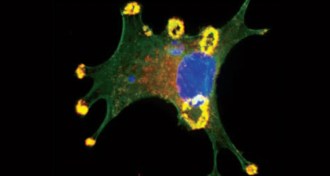
 Life
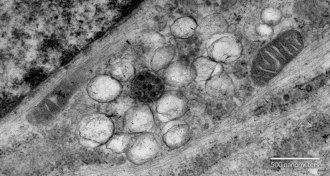
LifeDrug candidate takes new aim at MERS
An experimental drug that shuts down construction of virus-making factories could become a new weapon against MERS.
By Meghan Rosen -

-
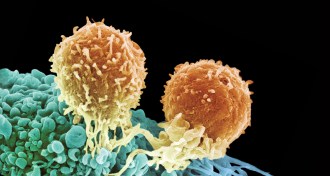 Life
LifeDesigner T cells emerge as weapons against disease
Decades of attempts to boost the immune system’s ability to fight disease are finally starting to pay off. Reprogrammed T cells serve as new weapons against cancer and autoimmune diseases.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLegalization trend forces review of marijuana’s dangers
Marijuana legalization advocates tout pot’s medicinal benefits and low addictiveness, while critics point to its neurological dangers. Research shows that the reality is somewhere in the middle.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOtters provide a lesson about the effects of dams
A dam created a new habitat, but that habitat’s lower quality kept otter density low.