Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeInsulating sheath on nerve cells isn’t an even coat
Myelin doesn't evenly coat axons, a finding that runs counter to what scientists suspected.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCloning produces stem cells from adult skin
Human embryonic stem cells made using adult cells could enable medical advances such as replacement organs.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew tools reveal new truths about fungi, flies, antibiotics
In the newsroom, any story about a new scientific method faces an uphill battle. In this issue are a number of stories that feature how science is done.
By Eva Emerson -
 Life
LifeThe name of the fungus
A rebellion has broken out against the traditional way of naming species in the peculiar, shape-shifting world of fungi.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene variant, processed meat linked to boost in cancer risk
In people with a specific variation of a gene on chromosome 10, eating processed meat is associated with an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePoor slumber is bad for young flies’ brains
A child's sleep deprivation could alter brain development and adult behavior, a study of fruit flies suggests.
-
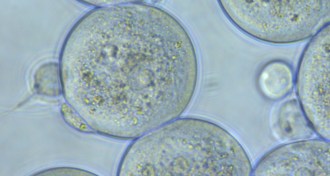 Life
LifeProtein that gets sperm into egg identified
The protein Folr4 on a reproductive egg plays this crucial role in the fusion of the sperm and egg, research shows.
-
 Tech
TechTo do: Exhibits to explore this May in D.C. and New York
Events include a celebration of science and original watercolor paintings from John James Audubon.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEven with rest, brain changes linked to football linger
The offseason may not allow enough time for football players' brains to heal from hard hits.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a chimp goes mattress hunting
Chimpanzees prefer firm beds made of ironwood, a new study finds.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly meat-eater may have led to larger plant-eaters
The newly identified Eocasea martini may have set the stage for later, much larger animals to become plant-eaters.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene activity sets humans apart from extinct hominids
Differences in gene activity caused by DNA methylation distinguish modern people from Neandertals and Denisovans.